Outline
ToggleIntroduction
The 555 Timer IC is one of the most popular and most frequently used integrated circuits. It performs an array of timing tasks in the electronic circuits and there is a huge list of experiments which can be performed with 555 IC. That is why it is very popular among electronics hobbyists.
But before using the 555 Timer IC, you should check it i.e. whether it is working properly or not. So, in this project, I have designed a simple circuit that can be used as a 555 Timer IC Testing Circuit and determine whether the 555 IC is functioning or not.
If you are stating with 555 Timer IC, then read this beginner’s tutorial on 555 TIMER IC.
A Brief Note on 555 Timer IC
I won’t go into the details about the 555 Timer IC but a few important things you need to need before understanding how the 555 Timer IC Testing Circuit works. The first important thing is that the 555 IC is available in 8-pin Dual-in-line Package (DIP) (or atleast it is the one I will be using in this project).
The second important thing about 555 Timer IC is that it has three modes of operation: Astable, Monostable and Bistable. The circuit implemented in this project is basically an Astable Mode of operation of the 555 Timer IC.
Principle
This simple 555 IC testing circuit can be used to test your entire 555 timer IC collection. So, before using your IC in any project, make sure that your IC is good or bad by testing it. This can be done by configuring the IC to act as an oscillator i.e. 555 is configured in Astable mode of operation.
The 555 tester circuit will rapidly tell you if the timer is functional or not. Important feature of this circuit is it will tell 555 timer is shorted or it is not oscillating.
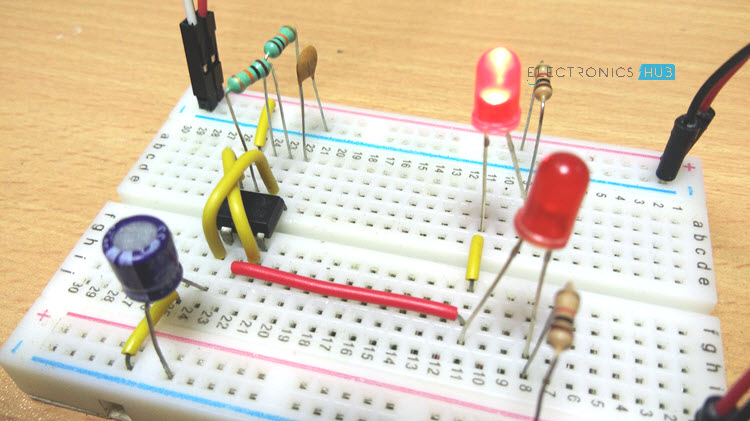
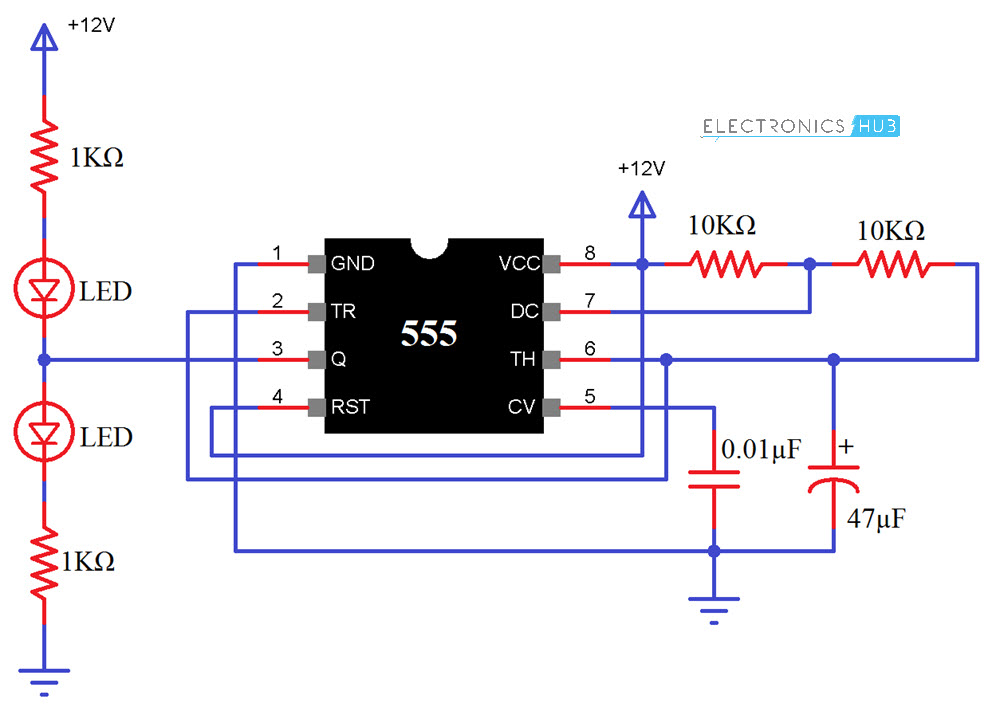
Simple 555 Timer IC Testing Circuit Diagram
The circuit diagram of the 555 testing circuit is shown in the image below.
Components Required
- 555 IC (IC under test)
- 8 Pin IC Holder
- 2 X 10KΩ Resistors
- 2 X 1KΩ Resistors
- 47μF Capacitor (Electrolytic)
- 0.01μF Capacitor (Ceramic Disc)
- 2 X LEDs
- 12V Power Supply
- Mini Breadboard
- Connecting Wires
Circuit Design
As mentioned earlier, I am going to use the 555 IC in its Astable Mode of operation. If you are familiar with this mode, then you can easily design the circuit yourself.
First, connect Pins 4 (Reset) and 8 (VCC) to +12V Supply and Pin 1 (GND) to GND. Short Pins 2 (TRIG) and 6 (THRESHOLD). Now, connect a 10KΩ Resistor between VCC and Pin 7 (DISCHARGE). This resistor will be called R1.
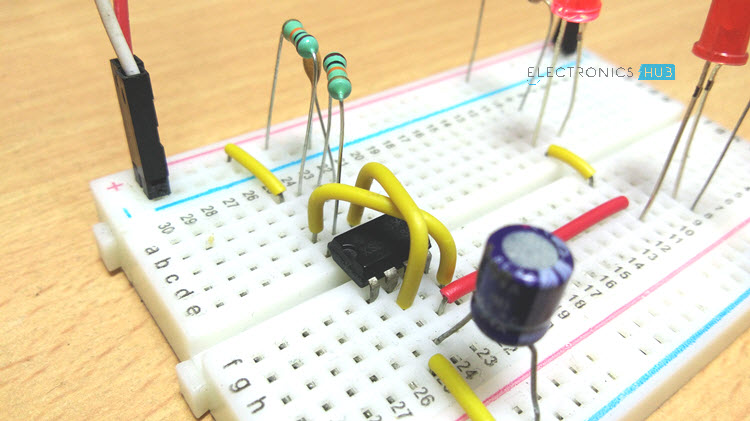
Also, connect another 10KΩ Resistor between Pin 7 and Pin 6. This resistor will be called R2. A 47μF Capacitor (here after called as C1) is connected between Pin 2 and GND.
An optional connection is to connect a 0.01μF Capacitor between Pin 5 (CONTROL) and GND. Finally, connect two LEDs as shown in the circuit diagram to Pin 3 (OUT) of the 555 Timer IC.
How to Check the 555 Timer IC?
First of all, insert the IC in socket (if used) very carefully so that no pin of 555 timer gets damage. Now to see the result, switch on the power supply. If your 555 timer is working properly, then both the LEDs (Red LEDs in my case) will glow alternately. If any of the LED is OFF or both the LEDs are not glowing, it means that your 555 timer IC is faulty.
Working of 555 Timer IC Tester Circuit
In this circuit, I have used the 555 IC as an Astable multivibrator and when power is provided to circuit, the LEDs will start blinking, which means that the IC is working. The blinking rate of LEDs can be changed by increasing or decreasing the values of resistor R1 and R2 and capacitor C1.
You can calculate the time duration with the help of formulae given below.
ON Time (HIGH) in Seconds = 0.693 * (R1 + R2) * C1
OFF Time (LOW) in Seconds = 0.693 * R2 * C1
Total Time Period in Seconds = 0.693 * (R1 +2R2)*C1
Frequency = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2R2) * C1)
As per our circuit, R1=10KΩ, R2=10KΩ and C1=47μF. If you substitute these values in the above equations, you will get the following results.
Frequency = 1.023 Hertz
ON Time = 0.651 Seconds
OFF Time = 0.326 Seconds
Time Period = 0.977 Seconds
You can see this in the following video.
Now coming to working, as soon as power supply is provided, C1 will start charging through R1 and R2. When the voltage across C1 rises above 2/ 3 of supply voltage, the internal Flip Flop toggles. As a result, pin 7 becomes low and C1 starts discharging.
When the voltage across C1 goes below 1/ 3 of supply voltage, the internal Flip Flop resets and pin 7 goes high. The C1 starts charging again. All this will happen only when your IC is in good condition. Based on the charging and discharging times of the Capacitor (as set by R1, R2 and C1), the output will stay HIGH or LOW and the LEDs will flash accordingly. From these observations, we can conclude that 555 Timer IC is faulty or not.
Related Post: Touch ON and OFF Switch Circuit


10 Responses
I AM LOOKING FOR A FREQ READER THAT CAN READ AND COPY 434 FREQ TRANSMITTERS AND CODE HOPPING TX, IF A CUSTOMER BRINGS A 434 OR CODE HOPPING TX I MUST BE ABLE TO COPY THE CODE TO ANOTHER TX PLEASE HELP
REGARDS
ROY
Built it to test twenty 555’s I just bought. I only changed R1,R2 and C2 because I didn’t have those values right at hand and made it little faster. Thanks
WHY DOES THE PRINT SHOW R3/R4 AS 220 E, AND THE PARTS LIST SHOW
20E?? WHAT DOES THE E STAND FOR??
E stands for ohm
similarly
k stands for kilo ohm M stands for mega ohm
Yes 100 % true, but all persons can not understand this
Thankyou
E stands for ohm
Both the LEDs are blinking simultaneously. Is that correct or should they remain continuously on.
And without the icon thebcircuit should the LEDs come on?
E is not the symbol for Ohm (“Omega” is the proper symbol) !
Is led 1 connected directly to pin one, as shown, or should a “bridge” be there?
According to the instructions, you state to put the 47u cap between pin 6 and GND, but the photo shows it on Pin 2. Pin 2 is correct. Also, make sure that one LED is connected to PWR and one to GND in order for them to blink out of sync or else they will blink at the same time.
Thanks for the circuit!
—>Sean