Solar or Photovoltaic System is a method of converting Solar Energy into Electric Energy using a principle known as the Photovoltaic Effect. Basically, it consists of Photovoltaic Cells (or Solar Cells), which are essentially made from a semiconductor material, that convert the Photons into electric energy. To maximize the capture of Solar Energy by these PV Cells, you need a proper Installation of Solar Panels with right number of panels, proper mounting type, orientation and direction of panels and many more.
In this guide, let us take a closer look at Solar Panels and understand How to Install Solar Panels, what are the different mounting styles, and many more.
Outline While the conventional (non-renewable) fuels such as coal, diesel, and petrol are still the dominating and main sources of energy, alternative energy sources such as Solar, Wind and Bio-energy, which are renewable, are slowly marking their territory. Of all the available renewable energy sources, Solar is abundant, easy to implement and install and is essentially free (once you recoup the initial investment). As a result, Solar Energy Systems are one of the top choices for alternative energy and are becoming increasingly popular. The process of converting light to electricity is known as Photovoltaic Effect. Photovoltaic Modules or Solar Cells are made from Silicon, a semiconducting material that is responsible for flow of electrons when Sunlight is incident on it. Solar Panels produce Direct Current or DC. Also, the voltage of output fluctuates slightly depending on the intensity of the Sunlight. Hence, apart from the Solar Panels, we need additional components such as a controller that properly regulates the output voltage and an inverter to covert the DC to AC (as most household appliances run on AC Power). Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of Solar Energy System. There are essentially three types of Solar Energy System Installations. They are: The Grid-Tied Solar System is a simple and affordable Photovoltaic System. There is no backup or battery in this system as the PV System connected to your existing grid supply. If your Solar Energy production is more than what you need, the controller (or a similar intelligent device) feed the excess power to the grid system and you get credits. But during night time when the solar generation is minimal, the system automatically pulls the necessary power from the grid. An Off-grid PV System, as the name suggests, is a completely independent and isolated system that has to tie ins to the grid. This setup is the most expensive as you need a battery bank to store the energy and use it when required. It is suitable for motor homes and remote location installations. The last popular type is a combination of the above two where you get the benefit of battery back up and also a tie in to the grid. You can charge the batteries during day time and if there is an excess power, then the system will feed it back to the grid. When the Solar generation is low or the battery pack is running low on juice, then you can draw the necessary power from the grid. Here are the typical steps involved in the installation of Solar Panels. You need to make necessary calculations to determine the ideal position of the panels so that the panels receive maximum Sun light. Once the orientation and tilt angle are finalized, you need to make sure that there are shades from any nearby trees or buildings. Tip: For countries in the northern hemisphere, the ideal way to mount Solar panels is by facing them South. It is North for countries in the southern hemisphere. The tilt angle depends on the latitude and longitude. Another important thing to consider is whether you opt for a roof installation or ground installation. In case of roof installation, there are again two considerations: a Flat Roof or a Slanting Roof. The mounting mechanism for both these types vary. Coming to ground mounting, again you can consider a bracket mount or a pole mount. One you finalize the type of mount; you can now start with installing the necessary support structures for the panels. Once the support structure is properly mounted, you can start installing the solar panels. This involves correctly placing the solar panels on the support structure and properly securing them using nuts and bolts. After the mechanical installation of Solar Panels is done, we can now move to the electrical part. Properly terminate all the cables with necessary tools and make the connection as per pre-planned circuit. Once all the basic wiring of the Solar panels is done, now is the time to connect the panels to a Solar Inverter and/or Controller. If you are designing an off-grid system or grid-tied system with backup, then you need to build a battery pack depending on your energy/backup requirements. Once the battery pack is ready, connect the solar controller to the battery and the batteries to the inverter. For grid-tied systems (with or without backup), you need additional components such as a utility meter and a disconnect switch. Once you connect all the necessary modules and components, test the system, schedule an inspection and start using your Solar Energy System. Also Check: Do You Need Snow Guards For Solar Panels? A simple guide on installation of Solar Panels. Residential Solar Energy Systems are becoming extremely popular and with proper planning you can easily install the solar panels. Before installing solar panels, you need to decide on some important parameters such as the aim of your Solar Energy Generation, Budget, type of installation (grid-tied, off-grid or grid-tied with backup), mounting style (roof or ground) and many more. Once everything is worked out, then the installation of solar panel becomes very easy.Solar Energy: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
Disadvantages
Types of Solar Installation
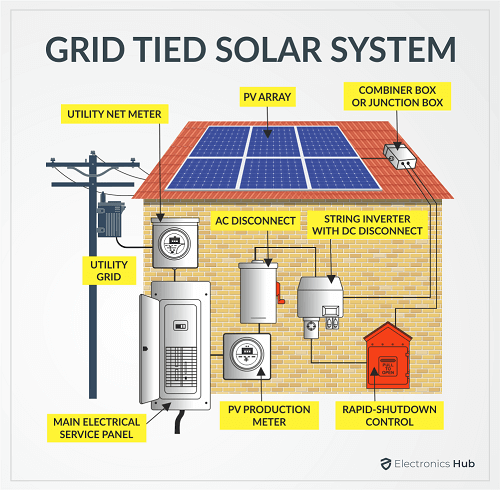
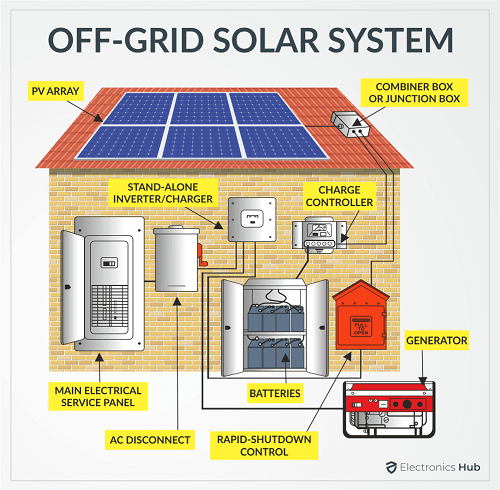
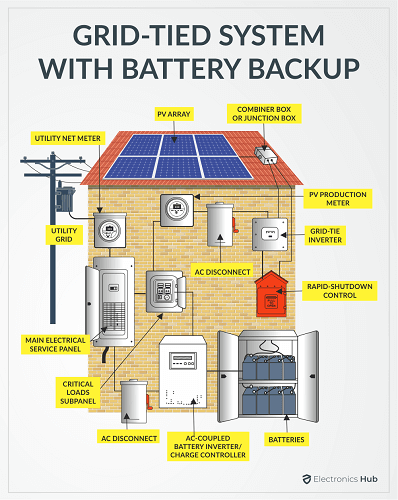
Typical Solar Installation Steps
Installation of Solar Panels
 In order to successfully install and operate your Solar Panels, you need a proper mounting system to firmly hold the panels and also correct wiring. So, the first step is to determine which mounting system to choose.
In order to successfully install and operate your Solar Panels, you need a proper mounting system to firmly hold the panels and also correct wiring. So, the first step is to determine which mounting system to choose.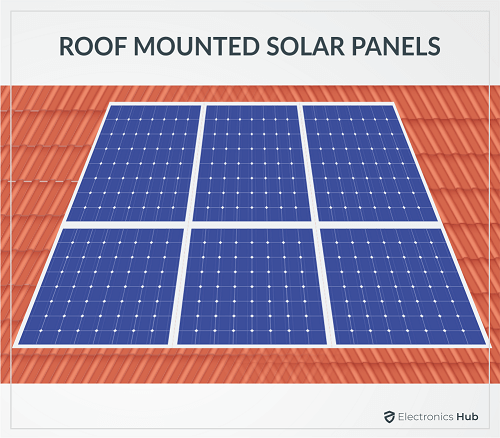
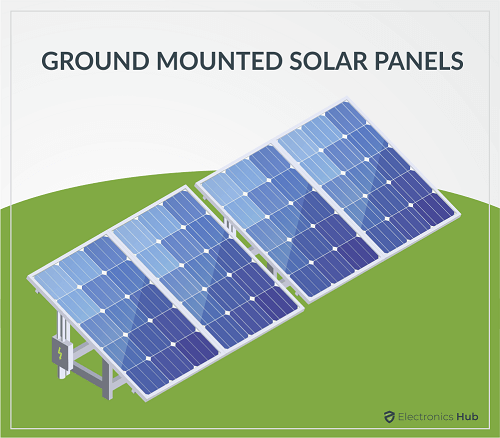
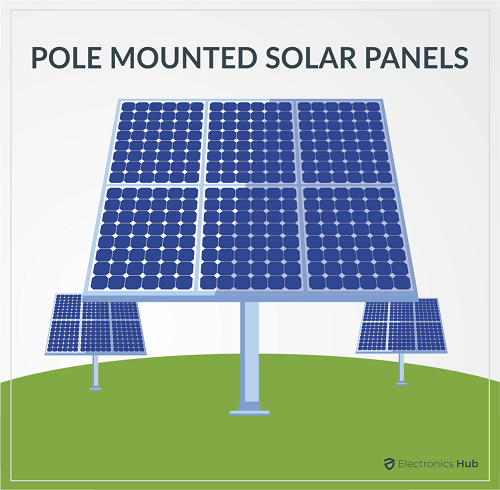
Conclusion:

