Tires are one of the critical components of an automobile. But sadly, they are also one of the most ignored parts of the car by many owners/drivers. A poorly inflated tire is not only a safety issue but it also affects the performance of the car, fuel economy and tire life.
Maintaining good (and proper) tire pressure as per the manufacturer’s suggestions will lead to a comfortable ride. A tire can lose its pressure due to any foreign objects such as nails, due to faulty valves, bad threads or even aging tires.
Every car owner must regularly monitor and maintain their car’s tire pressure. To assist them regarding this, several manufacturers are integrating Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) into the cars.
Outline
ToggleWhat is Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)?
TPMS or Tire Pressure Monitoring System as the name suggests, monitors the pressure of all the tires of a car and if any tire has low pressure, it illuminates a warning light in the instrument panel. As per the TREAD (Transport Recall Enhancement Accountability and Documentation) Act of 2000, all new car in the U.S. from 2008 must be equipped with a TPMS.
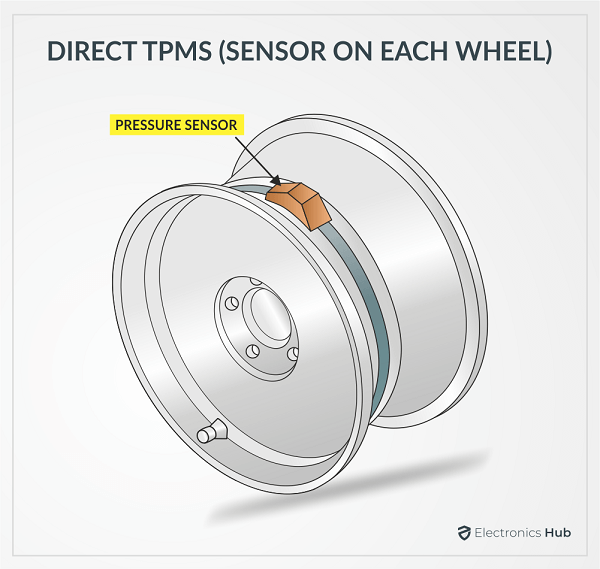
Some TPMS units have a sensor mounted on each valve stem while other units have a sensor strapped on to the center of each rim with the main sensing unit directly opposite to the valve stem.
Irrespective of the position of the sensor, they all detect the changes in the tire pressure and if it falls down below certain value, then the sensor units send an RF Signal to a receiver, which usually sits under the dash. This receiver unit communicates the car’s ECU and activates a warning light in the instrument panel.
Most modern implementations of TMPS are actually better as you can see the actual tire pressure of individual tires right in the instrument panel (usually on a small multi-information display) or in the infotainment screen.
Need for TMPS
Underinflated tires are one of the main causes of accidents. When the pressure is low, the tire gets damaged and this failure will increase the stopping distance or it will make the vehicle go out of control. The distance between the rim and the ground is about 10cm that is covered by air and tire layers. Due to this design, many drivers cannot easily judge the tire pressure properly.
A Tire Pressure Monitoring System helps the drivers by alerting them about underinflated tires. This system has been made mandatory in several countries/car markets such as the U.S, European Union, South Korea, Russia, Indonesia etc. We hope that several more countries try to mandate this safety feature as quickly as possible.
How Tire Pressure Monitoring System Works?
In order to understand how a typical Tire Pressure Monitoring System or TPMS works, we need to first take a look at the different types of TPMS. We can divide the TPMS available today into two types:
- Direct TPMS
- Indirect TPMS
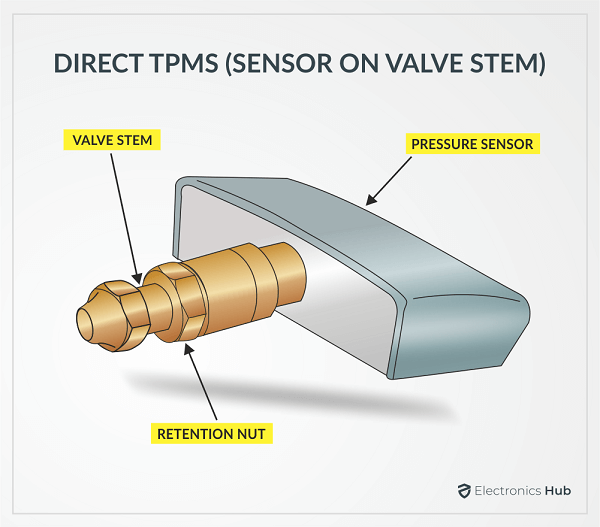
In a direct TPMS, each tire has its own pressure sensor, attached either to the valve stem (from the inside) or strapped on to center of the rim. This pressure sensor continuously monitors the tire pressure and the results will be shown on the driver’s display.
An indirect TPMS on the other hand uses the ABS wheel speed sensor to measure the speed of all tires and compares the differences between them. This system is not the most accurate one and is suitable for speeds up to 60mph.
We will now explore more about these two systems and understand how Tire Pressure Monitoring System works.
Direct TPMS
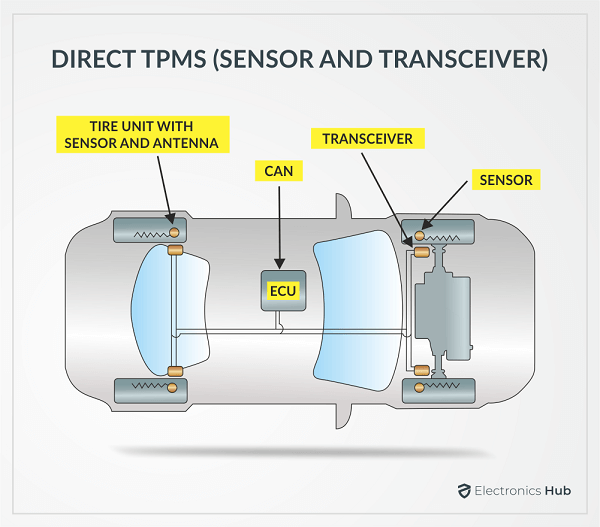
A Direct Tire Pressure Monitoring System (dTPMS) has four tire modules attached to the back of the valve stem (from the inside) of the four tires. A Tire Module is essentially a combination of three components.
- Piezo Resistive Pressure Sensor
- Signal Processing/Conditioning IC
- RF Transmitter
The pressure sensor is a MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) component made up of a silicon diaphragm sandwiched between two glass layers. Variations in pressure will cause the diaphragm to bow and other components will measure this mechanical strain.
If you are familiar with Sensors and Transducers, their output is very low, usually in microvolts. The signal processing IC will amplify this signal and also convert it into a digital value.
Next, an integrated or discrete UHF transmitter (based on SAW or PLL) will transmit the data to a receiver unit. A simple way to implement the TPMS receiver unit is to integrate it with the remote keyless entry system as they share similar functionality (and also to reduce cost). The receiver unit communicates with the ECU and displays the tire pressure on the driver’s display.
Indirect TPMS
While Direct Tire Pressure Monitoring System use individual and dedicated pressure sensors with each tire, the Indirect Tire Pressure Monitoring System (iTPMS) relies on existing ABS (Anti-Lock Braking System) to detect tire pressure. But how is this possible?
We know that one of the important jobs of the ABS Wheel Sensors is to detect its rotational speed. An Indirect TPMS makes use of this data. As the rotational speed of the tire is directly proportional to its pressure, a tire with low pressure has a lower diameter.
iTPMS calculates the difference between the rotational speeds of the tires and determines whether any tire has low-pressure or not.
Even though Indirect TPMS is less costly to implement than Direct Tire Pressure Monitoring System, the accuracy is not that great and it works better only if the car has 4-channel ABS. You can easily add an Indirect TPMS to a car with 4-channel ABS system at significantly less cost than a Direct TPMS.
Conclusion
Tire Pressure Monitoring System or TPMS is a safety feature on modern cars that continuously monitors the tire pressures and reports it to the driver if any tire is underinflated. We saw the basic of TPMS, different types of TPMS (direct and indirect) and also how Tire Pressure Monitoring System works.