Lights are actually an important part of our lives, no matter where you are, you will find yourself surrounded by some sort of man-made lighting. We are not talking about the old-school halogen bulbs here, it’s the era of LED lights.
And, why are we shifting to using LED lights more? The answer is pretty clear that LED lights are more energy-efficient and provide better illumination. However, have you ever wondered what’s the actual phenomenon LED lights use to glow? Well, if you are curious and interested to know how LED lights are made and work, make sure you read this article until the end thoroughly.
LED Materials
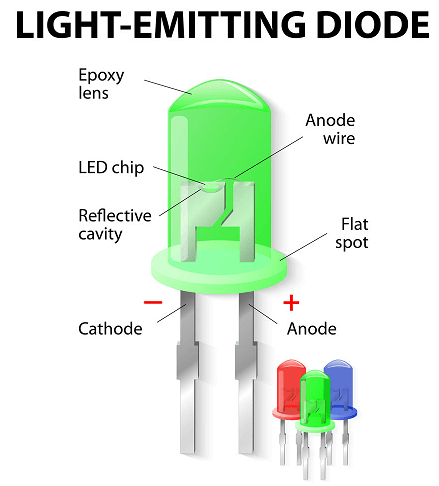
Unlike a halogen bulb, there are no long wires or filaments involved in LED lights. Instead, the LED lights glow because of the phenomenon known as electronic excitation. This is the actual reason why LED bulbs do not emit much heat like other kinds of lights. So, to understand the construction of an LED light, we must know about the materials used to make one. Basically, the LED term stands for light-emitting diode, and an LED light bulb consists of many such small-sized diodes.
Speaking of the diodes, each of them is made up of semiconductor material with two different layers having different concentrations of electrons. Usually, one of the layers has an excess of electrons, and the other one’s usually empty. Hence, when the current passes through the diodes, the electrons get excited and rush towards the empty layer. This to and fro motion of electrons rushing towards the empty layer is called electron excitation, which eventually makes the LED lights glow.
So, the phenomenon says, the LED will glow brighter and brighter if the electron excitation is more. For that to happen, the semiconductor material needs to be a good conductor of electricity. Although the semiconductor materials used in LEDs are made of crystalline materials, their electrical conductivity is increased by adding impurity during the manufacturing process. To understand this better, let’s take a simple example. You might know that water is a good conductor of electricity, but if you add salt (an impurity) to water, the conductivity increases. Hence, adding impurity enhances the quality of the semiconductor, not degrades it.
To make connections between the diodes, wiring is quite an essential part of the process. Although copper is known to be a good conductor of electricity, hence being used in most wires. Wires made of other materials like silver and gold are usually preferred in the case of LED lights since they are much better than copper in terms of quality. A lot of soldering work is required to make connections which can be done better with metals like gold and silver. At last, for the casing of the lights, using transparent plastic material adds durability to the light and makes it last for a longer time.
LED Design
Depending on your requirements, you are totally free to design an LED light without any boundaries. You can surely be creative while designing and choose the brightness, colours, colour temperatures, and other such factors as per your likings.
All such factors can be simply tweaked by selecting the right LED materials. For instance, the semiconductor material used plays quite a major role, as most of the illumination depends on the thickness of its layers and what quality of impurities are used to make it.
Manufacturing: How LEDs are Made
Since you know what materials are required to make an LED light, let’s check out how to join all those materials and make an LED light out of them. The manufacturing process of making an LED is a bit complicated though, but we’ll try to simplify it for you to understand better.
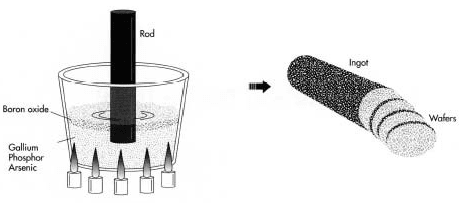
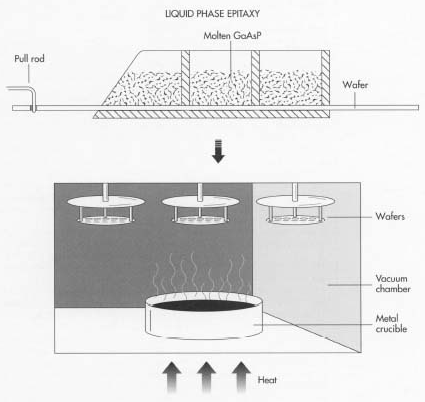
The main part of an LED light is the semiconductor material that needs to be made properly, we generally call it a semiconductor wafer. To make this, several elements like arsenic, gallium, phosphor are purified and kept in a chamber under high pressure and temperature until they get mixed up properly. Once the solution is ready, a rod is dipped into the solution and pulled out. This makes a crystalline layer of the solution stay on the rod.
Later on, the material is sliced off and filled into the semiconductor wafers. Once all the crystalline material is scraped off from the rod, it’s time to clean the rod, by sanding down and then keeping it in a cleaning solution to remove the material completely from its surface. This process is done multiple times until the semiconductor wafer is filled with multiple layers of the material. During the process of adding layers, impurities are also added to improve its conductivity.
Depending on the design, whether you are making a single LED or it’s going to be a cluster, metal contacts are designed accordingly. Lastly, the diodes are then connected to each other using proper wiring and encasing them into a transparent plastic cover for protection.
Final Words
LED lights have such a huge significance in our lives that we use them everywhere around us now. Even if you take a look at the back of your mobile phone, the flashlight our smartphones have is also an LED. It’s quite an interesting process by which LEDs are made, we believe you must have also found it quite interesting after going through this article.
Although the process seems easy to do, it takes a lot of effort and time to make one. Wrapping this up here, we hope you have liked this article so far, and if you did, don’t forget to share this knowledge with your friends and family. In case of any queries regarding LEDs, feel free to comment down below and let us know about them.