In this digital age where audio plays a significant role in our computing experience, the Analog Audio Front Panel (AAFP) header on motherboards takes center stage. The AAFP header is a standardized connector that allows for the seamless integration of front panel audio ports on your computer case with the motherboard’s audio subsystem.
With the AAFP header, you can easily connect headphones, microphones, and speakers to the front panel of your computer case, enhancing convenience and accessibility. No more reaching around to the rear of the motherboard to plug in your audio devices – the AAFP header brings audio connectivity to your fingertips.
In this guide, we will explore the significance of the AAFP header on a Motherboard, its functionality, potential issues you may encounter, and how to address them. We will look at the benefits of utilizing front panel audio ports, the differences between front and rear audio connections, and the compatibility considerations when working with the AAFP header.
Whether you are a seasoned computer enthusiast, a DIY builder, or someone curious about the inner workings of computer hardware, this guide aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the AAFP header and its role in enhancing your audio experience.
So, let us embark on this journey to unravel the world of AAFP headers and discover how they contribute to a seamless and immersive audio environment in your computer system.
Outline
ToggleFront Audio vs Rear Audio
Front audio refers to the audio ports located on the front panel of a computer case, typically near the top or front-facing side. These ports are designed for convenient access, allowing you to plug in headphones, microphones, or other audio devices without having to reach around to the rear of the computer.
Rear audio, on the other hand, refers to the audio ports located on the rear I/O (input/output) panel of the computer motherboard or sound card. These ports are usually color-coded and include connectors such as line-in, line-out, microphone, and speaker.
Here are some key points to consider regarding front audio and rear audio.
1. Convenience
Front audio ports are easily accessible on the front panel of the computer case, making it convenient to connect and disconnect audio devices.
Rear audio ports require you to reach around to the back of the computer, which may be less convenient depending on the positioning of your computer.
2. Cable Management
With front audio ports, you can route cables neatly within the case, reducing clutter. Rear audio ports may require longer cables that need to be routed from the back of the computer to your desk or audio devices.
3. Audio Quality
In terms of audio quality, there is typically no significant difference between front audio and rear audio. Both should provide the same audio fidelity if connected properly.
4. Interference
Depending on the design and construction of the computer case, front audio ports may be more susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) or noise from other components within the case.
Rear audio ports are generally further away from potential sources of interference, resulting in potentially cleaner audio signals.
When deciding whether to use front audio or rear audio, it often comes down to personal preference and convenience.
If you frequently switch between different audio devices or need quick access to headphone or microphone jacks, front audio ports can be more convenient.
However, if you have a dedicated audio setup or prefer a cleaner cable arrangement, rear audio ports may be preferable.
What is AAFP on Motherboard?
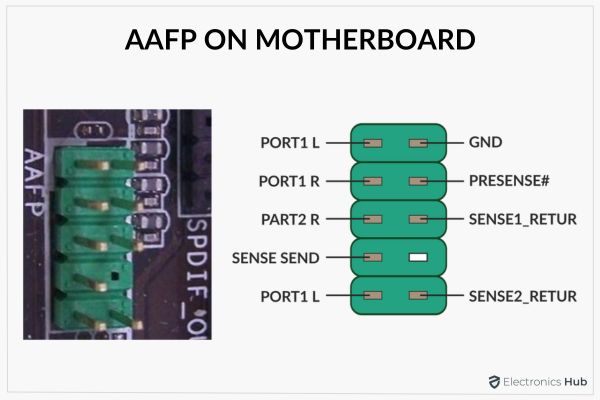 The term “AAFP” typically refers to the “AAFP header” or “AAFP connector” on a motherboard. AAFP stands for “Analog Audio Front Panel” and is a standardized connector used for connecting the front panel audio ports of a computer case to the motherboard.
The term “AAFP” typically refers to the “AAFP header” or “AAFP connector” on a motherboard. AAFP stands for “Analog Audio Front Panel” and is a standardized connector used for connecting the front panel audio ports of a computer case to the motherboard.
The AAFP header consists of several pins that correspond to different audio functions, such as microphone input, headphone output, and speaker output.
These pins are labeled and the pin configuration and labeling may vary slightly depending on the motherboard manufacturer, but the overall purpose and functionality remain the same.
The header allows you to connect the audio ports on the front of your computer case, such as the microphone and headphone jacks, so that they can be used for audio input and output. This enables you to use these ports for audio input and output conveniently.
It is important to note that “AAFP” refers to the connector or header, not to a specific motherboard model. Different motherboard manufacturers may have their own variations of the AAFP header, but the functionality is generally the same.
When choosing a motherboard, you’ll want to make sure it has an AAFP header if you plan to use the front panel audio ports on your computer case. Most modern motherboards, especially those designed for desktop systems, include an AAFP header as it has become a standard feature.
To connect the front panel audio ports of your computer case to the AAFP connector on the motherboard, you will typically use a compatible cable that comes with the case. The cable is designed to match the pin configuration of the AAFP connector and will have corresponding connectors for the microphone and headphone ports on the case.
Where is AAFP Located on Motherboard?
The location of the AAFP (Analog Audio Front Panel) connector on a motherboard can vary depending on the specific motherboard model and manufacturer. However, it is commonly found along the bottom edge of the motherboard, typically in the area where other front panel connectors are located.
To locate the AAFP connector on your motherboard, you can refer to the motherboard’s manual or documentation. The manual will provide a detailed diagram or description of the motherboard layout, including the location and pin configuration of the AAFP connector.
If you don’t have access to the manual, you can visually inspect the motherboard for a set of pins labeled for audio functions. Look for labels such as “AAFP,” “HD Audio,” or “Front Panel Audio.” These labels may be printed directly on the motherboard itself or in close proximity to the connector.
The AAFP connector is typically a rectangular or square-shaped header with multiple pins. The pins are usually arranged in a specific order, with each pin corresponding to a specific audio function such as microphone input, headphone output, or speaker output. The pin configuration may vary slightly depending on the motherboard manufacturer.
Remember, it is important to consult the motherboard’s manual or documentation for accurate and specific information regarding the location and pin configuration of the AAFP connector on your particular motherboard model.
How Does an AAFP Function?
The AAFP (Analog Audio Front Panel) functions as a connector or header on a computer motherboard that facilitates the connection between the front panel audio ports of a computer case and the motherboard’s audio subsystem.
It allows you to use the audio input and output ports on the front of your computer case for various audio devices such as headphones, microphones, or speakers. Here’s how the AAFP typically functions.
- The AAFP header consists of multiple pins that correspond to different audio functions. These functions may include microphone input, headphone output, speaker output, and potentially other audio-related features.
- You will use a compatible cable that is designed to connect the front panel audio ports of your computer case to the AAFP header on the motherboard. This cable usually comes with your computer case and is specific to its audio connector layout.
- The pins on the AAFP header are labeled and have a specific order or configuration. The cable’s connectors will match the pin configuration of the AAFP header, ensuring proper connection and functionality.
- Once the front panel audio ports are connected to the AAFP header, you can use them for audio input and output. For example, you can connect headphones to the front panel headphone port and use them to listen to audio. Similarly, you can connect a microphone to the front panel microphone port and use it for recording or communication purposes.
- The AAFP header allows the motherboard’s audio subsystem to detect and control the audio devices connected to the front panel audio ports. This includes adjusting volume levels, detecting microphone input, and enabling audio playback through headphones or speakers.
Remember that the specific pin configuration and labeling of the AAFP header may vary slightly depending on the motherboard manufacturer.
Therefore, it is recommended to consult your motherboard’s manual or documentation for accurate information regarding the pin configuration and functionality of the AAFP header on your specific motherboard model.
Importance of AAFP
The AAFP (Analog Audio Front Panel) is an important feature on a motherboard for several reasons.
1. Convenient Access
The AAFP allows for convenient access to audio ports on the front of your computer case. Instead of having to reach around to the rear of the motherboard to plug in headphones, microphones, or other audio devices, you can easily connect them to the front panel audio ports.
2. Enhanced User Experience
The AAFP improves the overall user experience by providing easy access to audio functionality. You can quickly connect and disconnect audio devices without the hassle of maneuvering cables at the back of your computer.
3. Accessibility
The front panel audio ports connected to the AAFP header are particularly useful for devices that require frequent audio plug-ins, such as headphones or headsets.
It saves you time and effort when you need to use audio devices for gaming, multimedia consumption, or communication.
4. Cable Management
By utilizing the front panel audio ports, you can keep cables organized within the computer case, reducing cable clutter. This contributes to better airflow, aesthetics, and overall system maintenance.
5. Multiple Audio Functions
The AAFP header supports various audio functions, including microphone input, headphone output, speaker output, and potentially other audio-related features. This versatility allows for a wide range of audio configurations to suit your needs.
6. Audio Quality
The AAFP header is designed to provide high-quality audio output. It supports modern audio standards, such as high-definition audio (HD Audio), which offers improved audio fidelity compared to older standards like AC97.
7. Compatibility
The AAFP has become a standard feature on modern motherboards. Most computer cases are designed with front panel audio ports that are compatible with the AAFP header, ensuring seamless integration and compatibility between the case and the motherboard.
Overall, the AAFP is essential for a convenient and efficient audio experience, enabling easy access to front panel audio ports, improving cable management, and providing high-quality audio output. It enhances the usability and versatility of your computer’s audio capabilities, making it an important feature on modern motherboards.
How to Connect AAFP?
To connect the front panel audio ports of your computer case to the AAFP (Analog Audio Front Panel) header on the motherboard, follow these general steps:
- Locate the AAFP header on your motherboard. It is typically positioned along the bottom edge of the motherboard and is labeled as “AAFP” or “Front Panel Audio.”
- Ensure that your computer case includes a front panel audio cable that is compatible with the AAFP header. The cable should have connectors for the front panel audio ports on one end and a compatible connector for the AAFP header on the other end.
- Check the pin configuration of the AAFP header and the connectors on the front panel audio cable. Pay attention to the labeling and pin arrangement to ensure proper alignment and connection.
- Gently insert the compatible connector on the front panel audio cable into the corresponding pins on the AAFP header. Take care to align the pins correctly, matching the pin configuration and labeling of the header. Ensure a secure and snug connection.
- Once the front panel audio cable is connected to the AAFP header, secure the cable using any cable management options available in your computer case. This will help keep the cable tidy and prevent it from interfering with other components.
- After connecting the cable, power on your computer and test the front panel audio ports. Plug in headphones or a microphone to verify that audio input and output are functioning correctly. Adjust audio settings in your operating system as necessary.
If you encounter any difficulties or have specific questions regarding your motherboard’s AAFP header, we recommended you refer to the motherboard’s manual or reach out to the manufacturer’s support for assistance.
Difference Between AAFP and AC97?
The main difference between AAFP (Analog Audio Front Panel) and AC97 (Audio Codec ’97) lies in their audio standards and the corresponding connectors.
AAFP
- AAFP is a newer standard for front panel audio connectivity on motherboards.
- It utilizes a 9-pin connector or header to connect the front panel audio ports of a computer case to the motherboard.
- AAFP supports high-definition audio (HD Audio) and provides improved audio quality compared to AC97.
- It supports features such as multiple audio channels, higher sampling rates, and enhanced audio codecs.
- AAFP is generally found on motherboards manufactured after 2004.
AC97
- AC97 is an older audio standard that was widely used in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
- It utilizes a 10-pin connector or header for front panel audio connectivity.
- AC97 supports standard audio quality and offers basic audio capabilities.
- It has a lower audio quality and lower sampling rates compared to AAFP.
- AC97 is commonly found on older motherboards.
AAFP and AC97 are not directly compatible with each other due to differences in their pin configurations and audio standards.
If you have a computer case with front panel audio ports designed for AC97, and your motherboard only has an AAFP header, you may require an adapter or converter to connect them properly.
AAFP is a newer standard that provides improved audio quality and features compared to the older AC97 standard. Check the specifications of your motherboard and computer case to ensure compatibility between the front panel audio ports and the motherboard’s audio header.
Common Issues with AAFP and How to Fix Them?
Here are some common issues related to the AAFP (Analog Audio Front Panel) header on a motherboard and potential solutions to fix them.
1. No Audio Output from Front Panel Ports
- Check if the front panel audio cable is properly connected to the AAFP header on the motherboard.
- Verify that the audio driver is installed and up to date. Download the latest audio driver from the motherboard manufacturer’s website.
- Check the audio settings in the operating system to ensure the correct audio device is selected and the volume is not muted.
- Try connecting headphones or speakers directly to the rear audio ports to determine if the issue is specific to the front panel ports.
2. Poor Audio Quality or Distortion
- Ensure that the front panel audio cable is securely plugged into the AAFP header.
- Check for any loose connections or damaged cables that could be affecting the audio signal.
- Test the audio quality by using different headphones or speakers to determine if the issue is with the audio device itself.
- Adjust the audio settings in the operating system, such as sample rate or audio enhancements, to optimize audio quality.
3. Microphone Not Working
- Check if the microphone is securely connected to the front panel audio port.
- Verify that the microphone is selected as the default recording device in the operating system’s audio settings.
- Ensure that the microphone is not muted or the volume is not too low in the audio settings.
- Test the microphone on another device to rule out any issues with the microphone itself.
4. Compatibility Issues with Older Cases
- Some older computer cases may have different pin configurations or wiring schemes for their front panel audio ports.
- In such cases, an adapter or workaround may be required to connect the front panel ports to the AAFP header.
- Check with the motherboard manufacturer or consult the motherboard manual for any specific instructions or compatibility considerations.
Conclusion
The AAFP (Analog Audio Front Panel) header on computer motherboards plays a vital role in providing convenient access to front panel audio ports. It allows you to easily connect headphones, microphones, and speakers to the front of your computer case, enhancing usability and accessibility.
By utilizing the AAFP header, you can eliminate the need to reach around to the rear of the motherboard, saving time and effort when connecting audio devices. This feature is particularly valuable for users who frequently utilize audio peripherals, such as gamers, multimedia enthusiasts, and individuals engaged in communication and content creation.
The AAFP header improves cable management within the computer case, minimizing clutter and promoting a clean and organized setup. It enhances the overall user experience by bringing audio connectivity to the forefront and providing seamless integration between the motherboard’s audio subsystem and the front panel audio ports.
While there may be potential issues and considerations with the AAFP header, such as interference or pin compatibility, these can generally be addressed through troubleshooting or following the guidelines provided by the motherboard manufacturer.
As technology advances, the AAFP header continues to be a standard feature on modern motherboards, ensuring compatibility with computer cases designed to support front panel audio ports. Its importance lies in its ability to enhance the audio experience, making it an essential consideration for anyone building or upgrading a computer system.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the AAFP header, its functionality, benefits, and potential issues. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently harness the power of the AAFP header to create a seamless and immersive audio environment tailored to your needs.

