A slow Wi-Fi connection can disrupt everything from video calls and online gaming to streaming and remote work. However, you can simply call your ISP and ask them to fix it for you. But, in some cases, even after getting it fixed from the ISP’s end, the problem persists. Maybe, the problem isn’t with your ISP but with something else at your end. Identifying the root causes of slow internet is essential to fix this issue.
In this guide, we’ll cover the common culprits behind slow Wi-Fi and provide straightforward solutions to address them. With numerous practical tips, you can effortlessly tackle this issue and enjoy a faster, more stable internet connection. Following these steps will eliminate frustrating delays and buffering for a seamless online experience.
Read on to improve your Wi-Fi signal speed and reliability.
Outline
Toggle- Why Is Your Wi-Fi So Slow?
- 1. Congested Network:
- 2. Router Location & Signal Interference:
- 3. Loose or Damaged Cables:
- 4. Firmware Update of Router:
- 5. Outdated or Inefficient Router:
- 6. Update Your Devices:
- 7. Malware or Security Breaches:
- 8. High Latency:
- 9. Data Cap Restrictions:
- 10. ISP Issues:
- 11. Maximum Speed of Internet Plans:
- 12. Limited Upload and Download Speeds:
- 13. Type Of Your Internet Connection:
- How To Fix Your Slow Wi-Fi Speed – 18 Ways To Resolve
- 1. Check Your Wi-Fi Speed:
- 2. Check Your Provider’s Network Facing Issues:
- 3. Restart Your Router:
- 4. Switch To 5GHz Frequency Band
- 5. Check Your Router Cables Are Damage Or Loose
- 6. Change Your Router Placement
- 7. Limit The Devices Connected To Your Wi-Fi Network
- 8. Change To A Different Channel
- 9. Update Or Reinstall Your Network Drivers
- 11. Change Your Wi-Fi Network Password
- 12. Update Your Router’s Firmware (If Available)
- 13. Update Your Devices
- 14. Check If You’re Using Any VPN
- 15. Reset Your Router
- 16. Upgrade Your Router
- 17. Consider Invest In a Mesh System Or Wi-Fi Extender
- 18. Contact your Internet Service Provider
- FAQs:
- Conclusion
Why Is Your Wi-Fi So Slow?
Slow Wi-Fi can disrupt your online activities. To help you address this issue, we’ve outlined the most common causes of a slow internet connection. For each potential cause, we provide a detailed explanation, enhancing your understanding and enabling you to identify and fix the problem effectively.
1. Congested Network:
If you overload your internet connection with data traffic more than it handles, then it results in network congestion. For instance, too many devices or applications like movie streaming, video calling, playing online games, or browsing using the same internet connection causes congestion.
To fix this issue, you need to either upgrade to a faster internet data plan or lower your internet usage. Remember that your ISP networks might be overloaded due to too much traffic and not enough bandwidth, resulting in slow Wi-Fi. Prefer to use the internet during off-peak hours
2. Router Location & Signal Interference:
A router that is placed too far will let you experience weak Wi-Fi signals. The reason is that the signal has to pass through obstructive materials (or) some electronic devices causing interference. Additionally, your Wi-Fi signal can interface with other Wi-Fi networks, particularly in densely populated areas where multiple networks operate on the same or nearby channels.
Besides this, the layout of your home will cause internet sluggishness (weaken or block the Wi-Fi signal). This makes the router’s placement quite essential for effective Wi-Fi signal to all the connected devices. So, to fix this issue, you need to choose a better spot to place the router, adjust the router’s settings (or) use Wi-Fi extenders/mesh system.
3. Loose or Damaged Cables:
Loose or damaged cables (Ethernet or coaxial cables) are another main cause of slow Wi-Fi or interruptions. Therefore, it is essential to check the cable’s conditions to see whether they might not be connected properly or damaged from excess kinks, stress, or damage from pets.
4. Firmware Update of Router:
Sometimes, the internet connection might slow down the Wi-Fi signal of your devices. In case, this slowdown is limited to certain devices, you probably focus on troubleshooting with those devices yet not your internet connection. However, a simple firmware update or restart of the router will clear this slow Wi-Fi issue.
5. Outdated or Inefficient Router:
The router’s age and efficiency will play a key role in how quickly your internet operates. So, it’s always better to upgrade to the newer, faster wireless Wi-Fi standards (802.11 ac or 802.11 ax are the latest versions). The older routers running on an outdated standard can’t grab the speed offered by your ISP.
Also, buying a new router doesn’t mean it will upgrade as per your requirements. Some are designed for basic tasks, while others are meant for demanding tasks. Checking with your ISP and upgrading to a more efficient router will make you enjoy online experiences.
6. Update Your Devices:
Outdated devices will sluggish your connection speed. These days, every gadget (from smartphones to laptops, and TVs) is built with software and hardware that might be outdated over time. As older devices are unable to update to the latest software or firmware (or) inefficient to support the latest version, then you can’t enjoy most of your internet speeds like performance enhancements or security updates.
7. Malware or Security Breaches:
If your device is attacked by any malware or viruses, it impacts the overall internet connection. The entered malware or virus will operate in the background and use your device’s internet connection, stealing your bandwidth. Further, it results in leaving you with less data to perform your regular online activities and causing a sluggish or unresponsive connection. Besides reduced speed, some malicious software redirects your internet traffic and delivers unwanted ads or engages in other activities exploiting your connection.
8. High Latency:
Latency is defined as the time taken for the data to transform from your device to the web server and back again. Simply, the waiting time for the page to respond after you click on the link. Usually, a low latency refers to faster online interactions, whereas a high latency results in noticeable delays.
The physical distance between the user and the website’s server will result in high latency. Other factors causing this high latency will be network congestion, poor routing by ISP, or other server-related issues. So, check these issues to resolve this high-latency issue.
9. Data Cap Restrictions:
Usually, we use ISP plans with limited data for every month. If you surpass this data cap due to frequent streaming, online gaming, downloads, or sharing your network with multiple users, then your internet connection slows down. Most times, the ISP will send a notification upon reaching your data cap, letting you know you reached the bandwidth throttling territory (monthly usage). It is advisable to contact your ISP to upgrade your plan with a higher data allowance.
10. ISP Issues:
Internet Service Provider (ISP) can throttle your internet speeds resulting in a slow connection via VPN. For this, run a speed test by connecting your computer/PC to a modem using an Ethernet cable. Also, open a VPN client to run the test again. If your VPN using connectivity is faster, then your ISP is throttling your service. This is because ISPs might throttle your speeds whenever they observe certain types of traffic, while VPN encrypts the data and connection, making the ISPs unable to check what you’re doing online. Additionally, the ISPs sometimes throttle your internet connection due to paid prioritization or forbidden activity.
11. Maximum Speed of Internet Plans:
The total bandwidth of your connection (internet speed) is measured in Mbps, and the ISP’s plans are advertised as up to XXX Mbps, even though they aren’t guaranteed. For instance, if you are paying for 600 Mbps per month, but you don’t enjoy the maximum due to various reasons like hardware issues, physical internet connection, buried cable, and connected devices communicating with multiple modems. So, we suggest you purchase a data plan that is a bit more than required for your daily online activities.
12. Limited Upload and Download Speeds:
It is quite common to upload and download data as a part of your online activities, like downloading temporary files from the site or uploading a rest to the website. If you are experiencing some systems of slow internet speeds without any downloading or streaming issues, then the issue might be with your upload speed.
In general, DSL, satellite, and cable providers offer less upload bandwidth than download bandwidth to their users. It will be an issue for streamers or heavy uploaders, who need to work on video and audio rather than sharing large files. Switching to a fiber plan is the best way to enhance your upload speeds, and the reason for this is that fiber-optic internet connections provide upload speeds equal to their download speeds.
13. Type Of Your Internet Connection:
Internet providers use different technologies (like fiber, cable, DSL, or satellite) to deliver internet connection, which in turn reflects in your overall Wi-Fi speeds.
- Satellite Internet – This technology will transfer the internet signals from a base station -> satellite -> receiver at your home/office (and vice versa). Since the information has to travel a lot, satellite internet has higher latency than other types of technologies. Thus, it simultaneously slows down the Wi-Fi signal.
- Cable Internet – It uses coaxial cable with higher bandwidth and its speed can reach up to 1200 Mbps, making it faster than DSL Internet.
- Fiber-Optic Internet – Being a new and best-wired connection, the fiber uses light pulses to send the internet data. It has low latency and can easily carry much more bandwidth than other types. It offers speeds up to 5000 Mbps, and less prone to network congestion, and provides equally high upload and download speeds.
- DSL Internet – This type uses phone lines to carry data, and is unable to handle the same bandwidth as cable or fiber does. Its electrical signals degrade in quality over distance and top out at just 100 Mbps.
Ultimately, cable and DSL are the most common internet types, while fiber is the new yet insufficient type. While Satellite is perfect for rural areas where the other types aren’t reachable.
How To Fix Your Slow Wi-Fi Speed – 18 Ways To Resolve
There may be plenty of reasons why a Wi-Fi connection might appear slow. It could be a faulty modem or router, too many connected devices at the same time, or some DNS server issue. Whatever the issue is, we will be discussing some effective fixes here that will help you utilize your Internet connection’s complete bandwidth.
Here are some effective ways to fix your slow Wi-Fi connection issues:
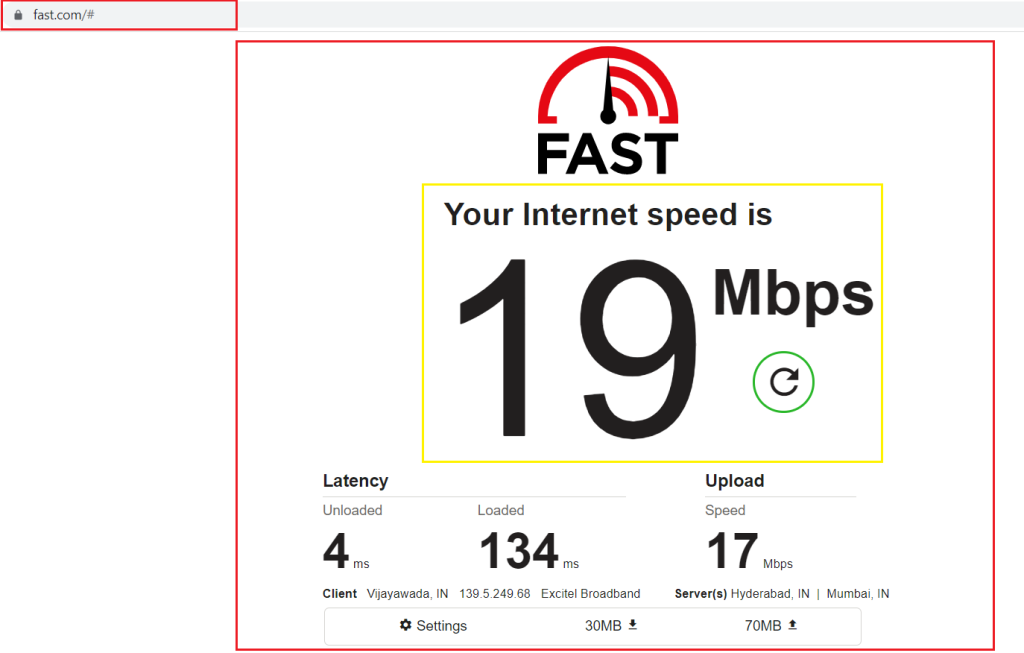
1. Check Your Wi-Fi Speed:
It’s important to regularly check your Wi-Fi speed, especially if your ISP has updated your plan or if you’re experiencing issues. it is always good to check your Wi-Fi speed by using websites like speedtest.net (or) fast.com, or just search Google to run your internet speed test. For this, you need to test the modem and router to troubleshoot where the problem lies.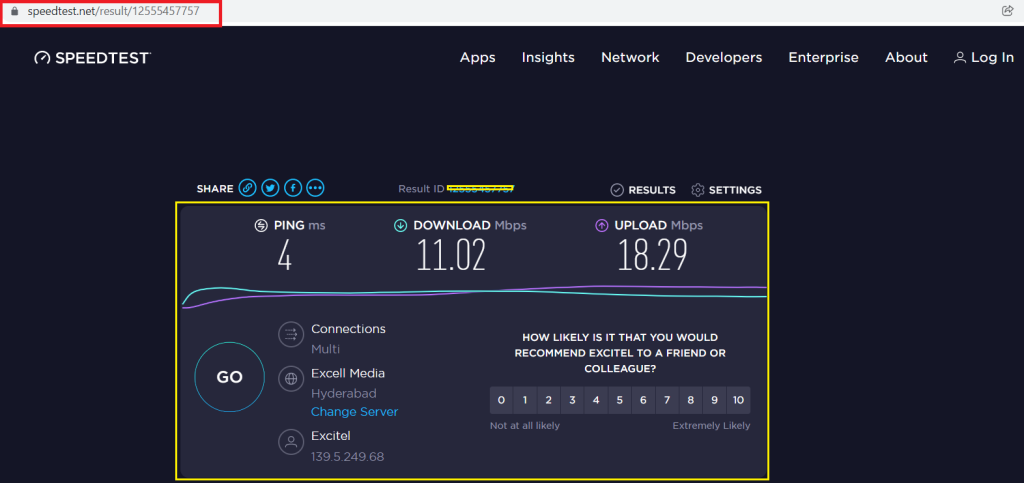
Also, check your ISP’s app to know how much speed your plan has each month and compare that number against the actual speed it provides. If the speed isn’t even close to the speed mentioned in the app, you can contact your ISP’s customer service. If there is no downtime or nothing wrong with your network from your ISP, then simply follow the other mentioned methods. Regular follow up will help to increase your internet speed and connectivity.
2. Check Your Provider’s Network Facing Issues:
Network congestion is one of the common culprits for Wi-Fi woes, and if this congestion gets even worse, then your internet provider throttles internet speeds to reduce traffic in your area. Even though this large-scale network congestion isn’t under control, yet you can resolve it by using the network during non-peak hours (nighttime). Also, consider switching your ISPs if the problem occurs quite often, and go with new services for enhanced internet.
Sometimes, your internet will slow down due to data cap limitations or if the provider is suspicious of your internet activity, as illegal or restricting you from performing a specific type of online activity (torrenting). In that case, run a speed test normally and use a VPN. if you find speed improves with the VPN, then you are throttled.
3. Restart Your Router:
As most tech experts mention a simple restart of your device (modem or router) will clear various minor internet troubleshooting issues. However, the process to restart the modem, router, or gateway will be the same. Here we have explained the method properly:
- The power cable of your device (found at the back of your modem, router, or gateway) should be unplugged to restart your device.
- Wait for a minute (60 seconds).
- Replug the power cable of the equipment
- Wait for the device to reboot properly (this may take up to 20 minutes).
This way you can easily restart your device and resolve most of the temporary glitches that cause Wi-Fi to slow down.
4. Switch To 5GHz Frequency Band
Generally, Wi-Fi routers support two different frequency bands – 2.4GHz, and 5GHz (some latest versions support 6 GHz). Both these network bands carry different bandwidths and have their own coverage area as well. Speaking of the 2.4GHz band, the internet signals on this band can travel up to a farther distance (wider coverage area) yet won’t provide faster Wi-Fi speeds, while 5GHz delivers much higher wireless Wi-Fi speeds, yet cannot travel quite far. So, the router with a dual-band frequency is perfect for those where a better internet speed is required.
Check whether you’re router is a dual-band unit by referring to a user manual or the router box – two SSIDs with the same name but different numbers 2.4GHz or 5GHz. If you’re using a tri-band router and your PC or other devices support this Wi-Fi 6E, then simply connect to the 6GHz SSID.
5. Check Your Router Cables Are Damage Or Loose
Even loose or damaged networking cables degrade your internet signal, cause signal interference, or cut off your bandwidth. So, it’s always better to check the cable’s condition to ensure proper connection.
Start checking with your Ethernet cables, which connect devices directly to your router (or) connect your router to the modem (if using a gateway model). Ensure that the cables are inserted properly in the modem/router or any devices connected directly to your router with an audible click sound. It is essential to check for any tears, kinks, any obvious wear signs, or any kind of damage that can’t be fixed, then replacing the cable with a proper alternative is the best option. If having an internet gateway and using Wi-Fi for all devices, then Ethernet cables aren’t used for checking.
The next essential cable to check is coaxial cable, especially if having cable internet. This cable delivers internet efficiently to your modem or gateway (combo). In case of having a fiber, then it could be a fiber-optic cable or Ethernet cable. This coaxial cable is at the back of the gateway or modem. Check if there are any signs of damage, it’s time to replace the cable to clear slow Wi-Fi issues.
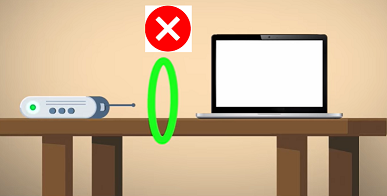
6. Change Your Router Placement
The placement of your router significantly influences your Wi-Fi’s speed and reliability. An outdated router might struggle to send a strong signal through walls, especially from metal, cement, or concrete. This can result in slower speeds and connectivity issues.
For optimal performance, consider moving your router to a central location in your home, ideally where it avoids barriers like walls and electronic devices that could disrupt the signal and cause interference. If your router is positioned far from your main devices, connecting to a 2.4GHz network can help, as it offers better range at the cost of speed. However, for faster connections close to the router, switch to a 5GHz network.
Check the signal strength on your devices—if you’re not getting at least three bars, it might be time to adjust your router’s position. Sometimes, simply shifting it a few feet can enhance the signal noticeably. If these adjustments don’t resolve the issues, consider upgrading to a more powerful router or adding an extender to boost the range and strength of your Wi-Fi network, ensuring reliable coverage across your home.
7. Limit The Devices Connected To Your Wi-Fi Network
In general, the bandwidth of the Wi-Fi network is shared between all the connected devices, and if a user consumes more bandwidth, then it surely impacts the other user and slows down their Wi-Fi. Some routers struggle with multiple simultaneous connections. So, set bandwidth limits to ensure all users enjoy adequate speeds.
To maintain fast internet speeds on your network, consider limiting the number of connected devices. Prioritize active devices and disconnect those not in use, as background apps can still consume bandwidth even when the device is inactive. This will help to balance network load, especially when high-bandwidth activities like 4K streaming, cloud gaming, or large downloads are in progress.
8. Change To A Different Channel
If you’re experiencing slow Wi-Fi, switching channels might help. Wi-Fi channels are meant to carry data on different frequencies, and some are more crowded than others. The reason for slow Wi-Fi problem is that you might be on a congested channel. Usually, modern routers with the latest Wi-Fi 5 or Wi-Fi 6 devices use 80 MHz channels, and you need to run a Wi-Fi diagnostic app to check the channels that are engaged or free. Mostly, the standalone routers let you change the channel in the mobile app or web interface (not on a mesh system). So, try to avoid heavily used channels. If you spot an underused non-overlapping channel, that’s your best option. Otherwise, opt for the second-best choice.
Changing channels is a straightforward process. Just log into your router’s management page—usually found at 192.168.1.1— go to network settings, and select a new channel. Refer to your router’s manual for further assistance to guide you. For Windows users, WifiInfoView by Nirsoft is a useful, free tool. It displays all Wi-Fi channels, indicating how busy each one is. Ultimately, choosing the least crowded channel will deliver a better experience.
9. Update Or Reinstall Your Network Drivers
If you are experiencing this slow internet speed issue only on a particular computer but not on any other devices, then it will surely be a driver issue. Generally, laptops with Windows OS get updated from time to time. If in case, the network drivers on your PC get missed or won’t update due to some reason, then you have to manually fix the driver issue on your computer to reinstall or update them properly.
For Windows System, you can update the drivers of a system running on Windows 10 OS by pressing the hotkey (Windows Key + X), and select Device Manager. Then the driver’s related information will be displayed in this section. Double-click on Network Adapter and select the one that you’re using now. Right-click on that and select the Update Driver option. This will auto-update the drivers on your Windows PC. Finally, restart the computer to confirm these changes.



For Mac devices, Apple itself will auto-update the drivers. But you need to check if these drivers are up to date or not. For this, click on the Apple icon on your Mac device and click on “System Preferences”. Go to Software Update, and then Update Now. In case, the Update Now isn’t found on your device, then simply means the drivers on your device are already up to date.
If this process doesn’t work on your system, look for an update for your driver on the manufacturer’s official drivers and utilities page. Usually, manufacturers publish the drivers on their official websites. You need to download the drive and double-click on the executable to install them. Finally, restart your computer to use the updated drivers.
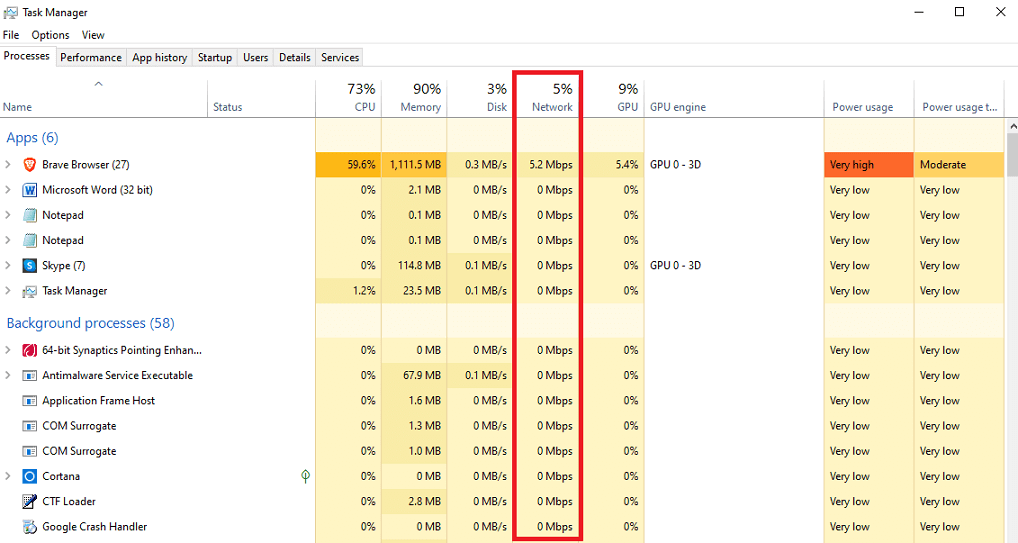
10. Check If Background Programs Using Heavy Bandwidths
Oftentimes, we forget to check for any bandwidth-heavy activities running in the background. There might be a Windows Update download or any app sucking the bandwidth or large file downloading in the background that we are unaware of while using the system.
To check which ongoing activities sucking up your bandwidth, you need to open the Task Manager via the hotkey (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) and go to Processes to observe CPU, Memory, Disk, and Network usage of your system. In that list, the Network column will notify you how much bandwidth is being used by all the ongoing activities.
You can halt any of those ongoing activities that aren’t important for you (or) simply delete any app that unnecessarily sucks up the bandwidth by right-clicking on the unused app and selecting the End Task button to clear it from your computer. Make sure programs like explorer.exe which won’t consume bandwidth should not be deleted. If done, your PC is rendered useless and needs a forced restart.
11. Change Your Wi-Fi Network Password
If none of the programs or devices consumes the bandwidth, yet you are experiencing slow Wi-Fi, there is a chance that someone hacked your network and using the bandwidth. This can often happen if the router uses an old security standard (or) WPS-enabled. WPA2/3 is the most advanced protocol to secure your wireless network.
Make sure to safeguard your network with at least a 12-digit strong password, and also you need to change the password quite often from the router’s main interface to prevent any unauthorized access, especially from neighbors or guests. For this, enter the IP address of the router in your browser’s address bar. Although, the common IP address will be 192.168.1.1 if you can’t find yours, here is the detailed procedure on how to find the default IP address.
- Press Windows + R to open Run and enter “cmd” to go to the command prompt (or simply enter Command Prompt in the Windows Settings).
- Type “ipconfig” and press enter.
- This will show the IP address next to the Default Gateway.
- Then enter this address in the browser address bar and click enter.
- Enter either 12345 (or) admin (refer to your router’s user manual or contact your ISP

Additionally, install a reliable antivirus solution to prevent any malware from taking advantage of your internet connection.
12. Update Your Router’s Firmware (If Available)
Keeping the router’s firmware up to date will enhance the overall Wi-Fi experience and troubleshoot issues like slow speed. So, updating your router’s firmware can significantly impact your Wi-Fi speed and signal strength. Here’s how to update the firmware:
- Regular firmware updates often include bug fixes that address issues affecting network performance, such as connection drops, slow speeds, or instability.
- Updated firmware strengthens your router’s security, protecting your network from cyber threats that can slow down your connection.
- Firmware updates can optimize your router’s performance, leading to faster speeds and more reliable connections.
- Some updates introduce new features, such as improved range, better bandwidth management, or advanced security options.
13. Update Your Devices
In some cases, the slow Wi-Fi isn’t caused by your internet connection, yet it might be due to your connected devices like tablets, computers, phones, or gaming consoles. You need to update an outdated one to process the enhanced Wi-Fi speeds. The Wi-Fi speed is reduced based on the router it connects to and the security protocol it uses.
If you are experiencing speed issues on a laptop or desktop, ensure to update to the latest OS and networking updates. Then power cycling the device will clear the junk memory, refresh the connection, and clean out temporary files or unnecessary processes. Also, shutting down the device completely for 30 seconds will clear this issue.
Other issues that might slow down your devices will include:
- Outdated software
- Too many opened applications
- Outdated drivers
- Too many opened browser tabs
- App downloads
- Reboot OS to install updates
- Patch downloads
- Malware
Close unused applications and browser windows to prevent overwhelming your system’s CPU. Also, an updated OS of the device by letting auto-updates, and ensuring a proper antivirus function.
14. Check If You’re Using Any VPN
VPN (Virtual Proxy Network) is widely used for anonymous browsing, yet you need to leave the VPN connection on when you’re browsing the net. Usually, these VPNs create tunnels to different countries and thereby the network speed and ping of this network won’t be nearly as fast as your normal connection speed. So, it is quite essential to disable the VPN connection to enhance your Wi-Fi speed on your devices.
15. Reset Your Router
A complete reset of your router to factory settings will revert any wrong changes affecting your Wi-Fi connection. Mostly, this tiny reset button is located at the back or side of the router. Press and hold his button for 10 – 15 seconds using a paper clip. This reset might delete all the memory and you need to go through this setup process again. Finally, you will enjoy your internet with an increase in your Wi-Fi speed than before.
16. Upgrade Your Router
An older router that uses outdated wireless technologies and limited transmission power isn’t worth troubleshooting for an enhanced Wi-Fi signal. Instead, it’s always better to invest in a new router with the latest Wi-Fi standards and features. This will improve the signal strength and aid in faster upload and download speeds.
17. Consider Invest In a Mesh System Or Wi-Fi Extender
If you are searching for a way to fix your slow Wi-Fi speeds other than replacing the existing router with a new one. Then you can simply invest in a Wi-Fi repeater or mesh system to your network. Here, the repeater works well to extend your Wireless Wi-Fi signal far in one direction. Whereas, a mesh system can cover multiple extra zones with a strong, seamless signal.
18. Contact your Internet Service Provider
If any of these quick fixes won’t resolve your slow Wi-Fi issue, then the final step is to contact your ISP and raise your ticket. They help you figure out whether the problem is from their end or your devices. Also, suggest some troubleshooting issues to resolve this problem (like upgrading your data plan). Furthermore, if the issue persists, the ISP can send their service agent over the place to fix this Wi-Fi woes (especially, if the problem is from their end).
FAQs:
Signs of Wi-Fi interference include slow speeds, frequent disconnections, and weak signal strength in certain areas. Other devices like cordless phones, microwaves, or neighboring Wi-Fi networks can cause interference.
The fluctuations in Wi-Fi speed can be caused due to network congestion, especially during peak usage hours. Multiple devices connected to the network, online activities of other users, and your ISP’s network traffic can impact speeds.
Your internet plan directly determines your maximum Wi-Fi speed. A faster plan allows for higher potential speeds, but other factors like Wi-Fi congestion and device capabilities also influence actual speeds.
A Wi-Fi dead zone is an area where the Wi-Fi signal is weak or non-existent. This can occur due to physical obstructions, distance from the router, or interference.
A strong Wi-Fi password prevents unauthorized access, which can slow down your network. Additionally, keeping your router’s firmware up-to-date and enabling encryption protocols like WPA3 can enhance security and performance.
Conclusion
A slow Wi-Fi connection can significantly hinder productivity and enjoyment. You can effectively troubleshoot and improve your wireless network with a proper understanding of common culprits like network congestion, interference, and outdated equipment. Implementing solutions such as optimizing router placement, managing connected devices, and updating firmware can help restore optimal Wi-Fi performance. Remember, a combination of factors often contributes to slow speeds, so a systematic approach to troubleshooting is key.
You can enjoy a faster and more reliable Wi-Fi connection with patience and the right steps. If the problem persists, feel free to contact your ISP and you can write to us in the below comments section. We’ll respond promptly to resolve your query and help you to enjoy a faster Wi-Fi connection.

 –
–