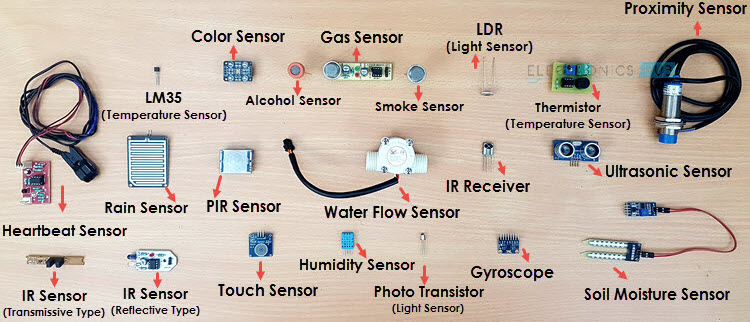
In our daily lives, sensors are everywhere, quietly working behind the scenes. Whether they’re in our homes, offices, or cars, these clever devices help simplify our routines. Imagine walking into a room and the lights automatically turn on, or your garage door opening by itself as you pull up the driveway—these are just a few examples of sensors at work. They not only make life easier but can also keep us safe by detecting dangers like smoke or fire.
Now, let’s take a moment to think about what sensors actually are, the different types we use, and how they fit into various applications. To kick things off, let’s consider a simple example of an automated system powered by sensors. It’s a great way to see the impact these small devices have on our world of automation and daily convenience.
Outline
Toggle- What Is A Sensor?
- Classification Of Sensors
- 25 Different Types Of Sensors And Their Uses
- Temperature Sensor
- Proximity Sensors
- Accelerometer Sensor
- Infrared Sensor (IR Sensor)
- Pressure Sensor
- Light Sensor
- Ultrasonic Sensor
- Flow and Level Sensor
- Smoke and Gas Sensors
- Microphone (Sound Sensor)
- Alcohol Sensor
- PIR Sensor
- Touch Sensor
- Color Sensor
- Humidity Sensor
- Position Sensor
- Tilt Sensor
- Strain and Weight Sensor
- Gyroscope Sensor
- Optical Sensor
- Capacitive Sensor
- Piezoelectric Sensor
- Thermal Sensor
- RFID Sensor
- Chemical Sensor
- Real Time Application Of Different Sensors
What Is A Sensor?
There are numerous definitions as to what a sensor is but I would like to define a Sensor as an input device which provides an output (signal) with respect to a specific physical quantity (input).
A Sensor is a device that converts signals from one energy domain to electrical domain. The definition of the Sensor can be better understood if we take an example in to consideration.
The term “input device” in the definition of a Sensor means that it is part of a bigger system which provides input to a main control system (like a Processor or a Microcontroller).
The simplest example of a sensor is an LDR or a Light Dependent Resistor. It is a device, whose resistance varies according to intensity of light it is subjected to. When the light falling on an LDR is more, its resistance becomes very less and when the light is less, well, the resistance of the LDR becomes very high.
We can connect this LDR in a voltage divider (along with other resistor) and check the voltage drop across the LDR. This voltage can be calibrated to the amount of light falling on the LDR. Hence, a Light Sensor.
Now that we have seen what is a sensor, we will proceed further with the classification of Sensors.
Classification Of Sensors
There are several classifications of sensors made by different authors and experts. Some are very simple and some are very complex.
In the first classification of the sensors, they are divided in to Active and Passive. Active Sensors are those which require an external excitation signal or a power signal. Passive Sensors, on the other hand, do not require any external power signal and directly generates output response.
The other type of classification is based on the means of detection used in the sensor. Some of the means of detection are Electric, Biological, Chemical, Radioactive etc.
The next classification is based on conversion phenomenon i.e., the input and the output. Some of the common conversion phenomena are Photoelectric, Thermoelectric, Electrochemical, Electromagnetic, Thermooptic, etc.
The final classification of the sensors are Analog and Digital, these produce an analog output i.e., a continuous output signal (usually voltage but sometimes other quantities like Resistance etc.) with respect to the quantity being measured.
Digital, in contrast to Analog, work with discrete or digital data. The data in digital sensors, which is used for conversion and transmission, is digital in nature.
25 Different Types Of Sensors And Their Uses
The following is a list of different types of sensors that are commonly used in various applications with examples. All these types are used for measuring one of the physical properties like Temperature, Resistance, Capacitance, Conduction, Heat Transfer etc.
| Type of Sensor | Used For |
|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor | Controlling HVAC systems in homes and offices |
| Proximity Sensor | Detecting objects in automatic doors |
| Accelerometer Sensor | Screen orientation in smartphones |
| IR Sensor (Infrared Sensor) | Remote controls for TVs and other devices |
| Pressure Sensor | Monitoring tire pressure in vehicles |
| Light Sensor | Adjusting screen brightness on smartphones |
| Ultrasonic Sensor | Parking assistance in cars |
| Flow and Level Sensor | Managing water levels in tanks |
| Smoke, Gas and Alcohol Sensor | Detecting smoke and gas leaks in homes |
| Microphone (Sound Sensor) | Voice recognition in smart speakers |
| Touch Sensor | Touchscreens on smartphones and tablets |
| Color Sensor | Color detection in industrial sorting machines |
| Humidity Sensor | Controlling humidity levels in greenhouses |
| Magnetic Sensor (Hall Effect Sensor) | Detecting the position of a rotating object |
| Position Sensor | Tracking the position of machine parts |
| Tilt Sensor | Detecting the tilt of gaming controllers |
| PIR Sensor | Motion detection in security systems |
| Strain and Weight Sensor | Weighing items on digital scales |
| Gyroscope Sensor | Stabilizing drones during flight |
| Optical Sensor | Adjusting lighting in smart home systems |
| Capacitive Sensor | Touchpads on laptops |
| Piezoelectric Sensor | Detecting vibrations in musical instruments |
| Thermal Sensor | Temperature control in ovens |
| RFID Sensor | Tracking inventory in warehouses |
| Chemical Sensor | Monitoring air quality |
Temperature Sensor
One of the most common and most popular sensors is the Temperature Sensor. A Temperature Sensor, as the name suggests, senses the temperature i.e., it measures the changes in the temperature.
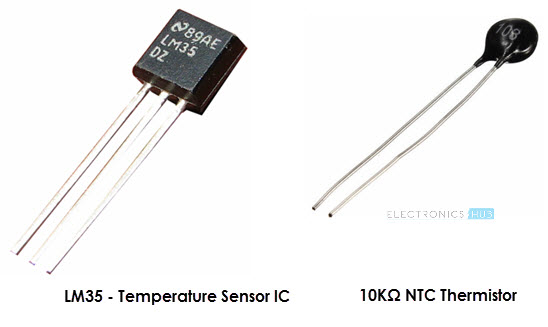
There are different types of Temperature Sensors like Temperature Sensor ICs (like LM35, DS18B20), Thermistors, Thermocouples, RTD (Resistive Temperature Devices), etc.
Temperature Sensors can be analog or digital. In an Analog Temperature Sensor, the changes in the Temperature correspond to change in its physical property like resistance or voltage. LM35 is a classic Analog Temperature Sensor.
Coming to the Digital Temperature Sensor, the output is a discrete digital value (usually, some numerical data after converting analog value to digital value). DS18B20 is a simple Digital Temperature Sensor.
Temperature Sensors are used everywhere like computers, mobile phones, automobiles, air conditioning systems, industries etc.
A simple project using LM35 (Celsius Scale Temperature Sensor) is implemented in this project: TEMPERATURE CONTROLLED SYSTEM.
Proximity Sensors
A Proximity Sensor is a non-contact type sensor that detects the presence of an object. Proximity Sensors can be implemented using different techniques like Optical (like Infrared or Laser), Sound (Ultrasonic), Magnetic sessor (Hall Effect sensor), Capacitive, etc.
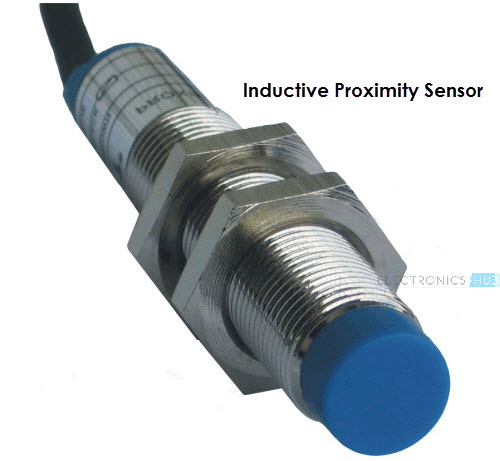

Some of the applications of Proximity Sensors are Mobile Phones, Cars (Parking), industries (object alignment), Ground Proximity in Aircrafts, etc.
Proximity Sensor in Reverse Parking is implemented in this Project: REVERSE PARKING SENSOR CIRCUIT.
Accelerometer Sensor
An accelerometer is a handy sensor that measures acceleration. It detects both the direction and the magnitude of acceleration, whether it’s from movement or the force of gravity.
These come in different types, such as capacitive or piezoelectric, each suited for specific applications. For example, capacitive accelerometers are commonly found in smartphones to detect orientation.
Accelerometers can output data in both analog and digital formats. A typical analog accelerometer will change its voltage output in response to movement. Digital models, like those in modern electronics, directly provide numerical data that applications can use.
You’ll find accelerometers in various devices, from mobile phones and tablets to cars, where they help with stability control and accident detection.
Infrared Sensor (IR Sensor)
IR Sensors or Infrared Sensor are light based sensor that are used in various applications like Proximity and Object Detection. IR Sensors are used as proximity sensors in almost all mobile phones.
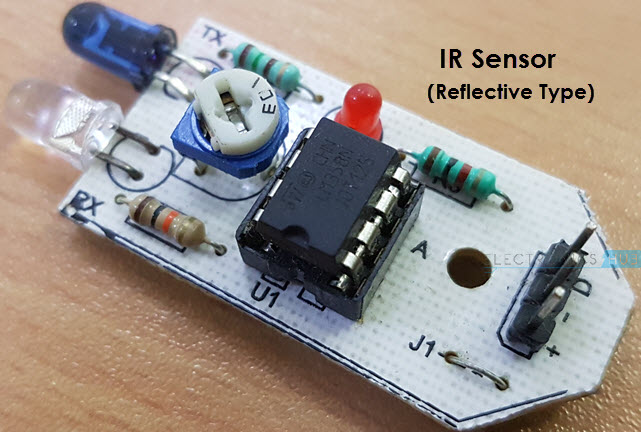
There are two types of Infrared or IR Sensors: Transmissive Type and Reflective Type. In Transmissive Type IR Sensor, the IR Transmitter (usually an IR LED) and the IR Detector (usually a Photo Diode) are positioned facing each other so that when an object passes between them, the sensor detects the object.
The other type of IR Sensor is a Reflective Type IR Sensor. In this, the transmitter and the detector are positioned adjacent to each other facing the object. When an object comes in front of the sensor, the infrared light from the IR Transmitter is reflected from the object and is detected by the IR Receiver and thus the sensor detects the object.
Different applications where IR Sensor is implemented are Mobile Phones, Robots, Industrial assembly, automobiles etc.
A small project, where IR Sensors are used to turn on street lights: STREET LIGHTS USING IR SENSORS.
Pressure Sensor
A pressure sensor is a tool that measures the force exerted by a fluid or gas. It can detect subtle changes in pressure and convert them into an electrical signal.
There are several types of pressure sensors, including piezoelectric, strain gauge, and capacitive sensors. Each type has its specialty. For instance, piezoelectric sensors are excellent for dynamic pressure measurements like sound waves.
Pressure sensors can also be analog or digital. In an analog sensor, the output is a continuous electrical signal that varies with the pressure. Digital sensors, on the other hand, convert this information into digital data that can be easily read by computers.
These are essential in many areas, such as weather forecasting, automotive systems, and even healthcare, where they monitor blood pressure or respiratory conditions.
Light Sensor
Sometimes also known as Photo Sensors, Light Sensors are one of the important sensors. A simple Light Sensor available today is the Light Dependent Resistor or LDR. The property of LDR is that its resistance is inversely proportional to the intensity of the ambient light i.e., when the intensity of light increases, its resistance decreases and vise-versa.
By using LDR is a circuit, we can calibrate the changes in its resistance to measure the intensity of Light. There are two other Light Sensors (or Photo) which are often used in complex electronic system design. They are Photo Diode and Photo Transistor. All these are Analog Sensors.
There are also Digital Light Sensors like BH1750, TSL2561, etc., which can calculate intensity of light and provide a digital equivalent value.
Check out this simple LIGHT DETECTOR USING LDR project.
Ultrasonic Sensor
An Ultrasonic Sensor is a non-contact type device that can be used to measure distance as well as velocity of an object. An Ultrasonic Sensor works based on the properties of the sound waves with frequency greater than that of the human audible range.

Using the time of flight of the sound wave, an Ultrasonic Sensor can measure the distance of the object (similar to SONAR). The Doppler Shift property of the sound wave is used to measure the velocity of an object.
Arduino based Range Finder is a simple project using Ultrasonic Sensor: PORTABLE ULTRASONIC RANGE METER.
Flow and Level Sensor
Flow and level sensors are all about keeping an eye on liquids and gases. Whether it’s measuring how fast something flows or checking how much is left in a tank, these are the go-to tools.
You might come across different kinds, like ultrasonic sensors that measure without touching the liquid, or float sensors that sit right in it and rise or fall with the level.
Whether they’re analog or digital, these sensors are super helpful. Analog versions give you a smooth signal that changes with the flow or level, while digital ones break it down into numbers that are easy to read and use.
From making sure your coffee machine has enough water to keeping factories running smoothly, flow and level sensors play a big part in our everyday tech.
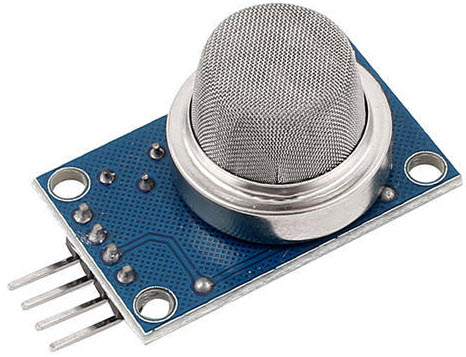
Smoke and Gas Sensors
One of the very useful sensors in safety related applications are Smoke and Gas Sensors. Almost all offices and industries are equipped with several smoke detectors, which detect any smoke (due to fire) and sound an alarm.
Gas Sensors are more common in laboratories, large scale kitchens and industries. They can detect different gases like LPG, Propane, Butane, Methane (CH4), etc.
Now-a-days, smoke sensors (which often can detect smoke as well gas) are also installed in most homes as a safety measure.
The “MQ” series of sensors are a bunch of cheap sensors for detecting CO, CO2, CH4, Alcohol, Propane, Butane, LPG etc. You can use these to build your own Smoke Sensor Application.
Check out this SMOKE DETECTOR ALARM CIRCUIT without using Arduino.
Microphone (Sound Sensor)
A microphone, often used as a sound sensor, captures sound waves and converts them into electrical signals. This transformation allows devices to analyze or amplify the sound.
Microphones come in various types, such as dynamic, condenser, and ribbon microphones, each suited for different applications. For example, condenser microphones are popular in studio settings for their sensitivity and high-fidelity recordings.
These sensors can be analog or digital. Analog microphones convert sound waves into a continuous electrical signal that mirrors the sound. Digital microphones, on the other hand, convert sound into digital data that can be easily processed by computers.
You’ll find microphones in a wide range of applications, from smartphones and computers where they help in communication, to professional audio equipment and hearing aids.
Alcohol Sensor
As the name suggests, an Alcohol Sensor detects alcohol. Usually, alcohol sensors are used in breathalyzer devices, which determine whether a person is drunk or not. Law enforcement personnel uses breathalyzers to catch drunk-and-drive culprits.
A simple tutorial on HOW TO MAKE ALCOHOL BREATHALYZER CIRCUIT?
PIR Sensor
A PIR (Passive Infrared) sensor is your go-to gadget for detecting motion. It works by picking up infrared light from objects in its viewing area. Whenever something warm, like a person or animal, passes by, it notices the change in infrared radiation and triggers a response.
These sensors are a key part of security systems, lighting controls, and energy-efficient devices. They’re fantastic for applications where you don’t want to bother with switching things on and off manually.
PIR sensors are simple but clever. They usually don’t output tons of data, just enough to tell you if there’s movement or not. This makes them incredibly efficient and reliable for everyday use in homes and businesses.
You’ll find them in alarm systems, automatic doors, and even in some toys, making them a common yet invisible part of modern life.
Touch Sensor
We do not give much importance to touch sensors but they became an integral part of our life. Whether you know or not, all touch screen devices (Mobile Phones, Tablets, Laptops, etc.) have touch sensor in them. Another common application of touch sensor is trackpads in our laptops.
Touch Sensors, as the name suggests, detect touch of a finger or a stylus. Often touch sensors are classified into Resistive and Capacitive type. Almost all modern touch sensors are of Capacitive Types as they are more accurate and have better signal to noise ratio.
If you want to build an application with Touch Sensor, then there are low-cost modules available and using those touch sensors, you can build TOUCH DIMMER SWITCH CIRCUIT USING ARDUINO.
Color Sensor
A Color Sensor is an useful device in building color sensing applications in the field of image processing, color identification, industrial object tracking etc. The TCS3200 is a simple Color Sensor, which can detect any color and output a square wave proportional to the wavelength of the detected color.
If you are interested in building a Color Sensor Application, checkout this ARDUINO BASED COLOR DETECTOR project.
Humidity Sensor
If you see Weather Monitoring Systems, they often provide temperature as well as humidity data. So, measuring humidity is an important task in many applications and Humidity Sensors help us in achieving this.
Often all humidity sensors measure relative humidity (a ratio of water content in air to maximum potential of air to hold water). Since relative humidity is dependent on temperature of air, almost all Humidity Sensors can also measure Temperature.
Humidity Sensors are classified into Capacitive Type, Resistive Type and Thermal Conductive Type. DHT11 and DHT22 are two of the frequently used Humidity Sensors in DIY Community (the former is a resistive type while the latter is capacitive type).
Checkout this tutorial with DHT11 HUMIDITY SENSOR ON ARDUINO.
Position Sensor
A position sensor detects the position of an object or point within its environment. It converts the position data into an understandable output, typically an electrical signal.
There are various types of position sensors, including linear position sensors, rotary position sensors, and angle sensors. Each type is tailored for specific applications. For example, linear position sensors are often used in manufacturing equipment to ensure precise movements.
Position sensors can be analog or digital. Analog sensors provide continuous data that changes linearly with the position. Digital sensors, however, output precise positional data in a format that digital systems can interpret easily.
These sensors play a crucial role in numerous fields, from robotics, where they help with precise control, to automotive systems, where they ensure optimal engine performance and safety.
Tilt Sensor
Often used to detect inclination or orientation, Tilt Sensors are one of the simplest and inexpensive sensors out there. Previously, tilt sensors are made up of Mercury (and hence they are sometimes called as Mercury Switches) but most modern tilt sensors contain a roller ball.
A simple Arduino based title switch using tilt sensor is implemented here HOW TO MAKE A TILT SENSOR WITH ARDUINO?
Strain and Weight Sensor
A strain and weight sensor measures the force or load applied to an object. It works by detecting the strain (deformation) that occurs when the object is under stress.
There are different types of these sensors, like strain gauges and load cells. Strain gauges are often used in mechanical testing, while load cells are commonly found in scales and industrial weighing systems.
These sensors can be either analog or digital. An analog sensor produces a signal that varies with the force applied, while a digital sensor converts this signal into readable data.
Strain and weight sensors are used in many areas. You’ll see them in bathroom scales, kitchen scales, and industrial equipment where precise weight measurement is crucial. They help ensure accuracy in manufacturing, packaging, and even in everyday household items.
Gyroscope Sensor
A gyroscope sensor measures the orientation and rotation of an object. It helps track how an object is spinning or turning in different directions.
Gyroscopes come in various forms, including mechanical, optical, and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) gyroscopes. MEMS gyroscopes are the most common today, found in many consumer electronics.
These sensors can be either analog or digital. Analog gyroscopes produce a continuous signal that varies with the rotation, while digital gyroscopes convert this information into data that can be easily read by devices.
Gyroscope sensors are essential in many devices, from smartphones and gaming controllers to drones and car navigation systems. They help with tasks like screen orientation, motion sensing, and maintaining stability in flight.
Optical Sensor
An optical sensor detects light and changes in light intensity. It converts this information into an electrical signal that devices can understand.
There are different types of optical sensors, like photodiodes, phototransistors, and CCDs (Charge-Coupled Devices). Each type is suited for various tasks, such as detecting light levels, measuring distances, or capturing images.
These sensors can be analog or digital. Analog optical sensors produce a signal that varies with the light intensity, while digital sensors convert light into digital data for easier processing.
Optical sensors are used in many everyday applications. You’ll find them in devices like remote controls, smartphones, and safety systems, where they help detect movement, measure distances, or adjust screen brightness automatically.
Capacitive Sensor
A capacitive sensor detects changes in capacitance to measure the proximity or touch of an object. It works by sensing the electrical properties of the object it comes into contact with.
There are various types of capacitive sensors, such as touch sensors used in touchscreen devices and proximity sensors that detect objects without direct contact.
These sensors can be analog or digital. Analog capacitive sensors produce a continuous signal that changes with the capacitance, while digital sensors convert this information into digital data for easy interpretation.
Capacitive sensors are found in many everyday devices. They’re used in smartphones, tablets, and touchpads to detect touch inputs. They’re also used in industrial applications to detect the presence of materials without physical contact.
Piezoelectric Sensor
A piezoelectric sensor measures changes in pressure, acceleration, temperature, strain, or force by converting them into an electrical charge. It works using the piezoelectric effect, where certain materials generate an electric charge when mechanically stressed.
There are various types of piezoelectric sensors, such as those used for measuring vibration, detecting impact, or monitoring pressure changes. These sensors are highly sensitive and can detect even minor changes in the environment.
Piezoelectric sensors can be found in both analog and digital forms. Analog sensors produce a continuous signal that varies with the force applied, while digital sensors convert this signal into readable data for easy analysis.
You’ll find piezoelectric sensors in many applications, from musical instruments like electric guitars to industrial machines, medical devices, and everyday items like microwave ovens, where they help detect touch or vibration.
Thermal Sensor
A thermal sensor measures temperature by detecting thermal radiation or changes in heat. These sensors are essential for monitoring and controlling temperature in various applications.
There are different types of thermal sensors, including thermocouples, thermistors, and infrared sensors. Each type has its own specific use. For example, infrared sensors can measure temperature from a distance without direct contact.
Thermal sensors can be analog or digital. Analog sensors provide a continuous signal that varies with temperature changes, while digital sensors convert this information into digital data that can be easily read and processed.
You’ll find thermal sensors in a wide range of devices, from household appliances like ovens and refrigerators to industrial equipment and medical devices where precise temperature control is crucial.
RFID Sensor
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) sensor uses radio waves to read and capture information stored on a tag attached to an object. It helps in tracking and identifying items without needing direct contact or a line of sight.
RFID sensors come in different types, such as passive RFID, which relies on the reader’s signal for power, and active RFID, which has its own power source for a stronger signal and longer range.
These sensors can be found in both analog and digital formats. Analog RFID sensors generate a continuous signal, while digital RFID sensors convert this signal into data that can be easily processed by computers.
You’ll see RFID sensors in various applications, from inventory management and asset tracking in warehouses to contactless payment systems and even pet microchipping.
Chemical Sensor
A chemical sensor detects and measures the presence or concentration of chemical substances in an environment. It converts this chemical information into an electrical signal for analysis.
There are various types of chemical sensors, including electrochemical sensors, optical sensors, and semiconductor sensors. Each type is suited for different applications. For example, electrochemical sensors are often used for detecting gases like carbon monoxide or oxygen.
Chemical sensors can be analog or digital. Analog sensors produce a continuous signal that varies with the concentration of the chemical, while digital sensors convert this information into digital data for easy processing and interpretation.
You’ll find chemical sensors in a wide range of applications, from environmental monitoring and industrial processes to medical diagnostics and safety systems in homes and workplaces.
Real Time Application Of Different Sensors
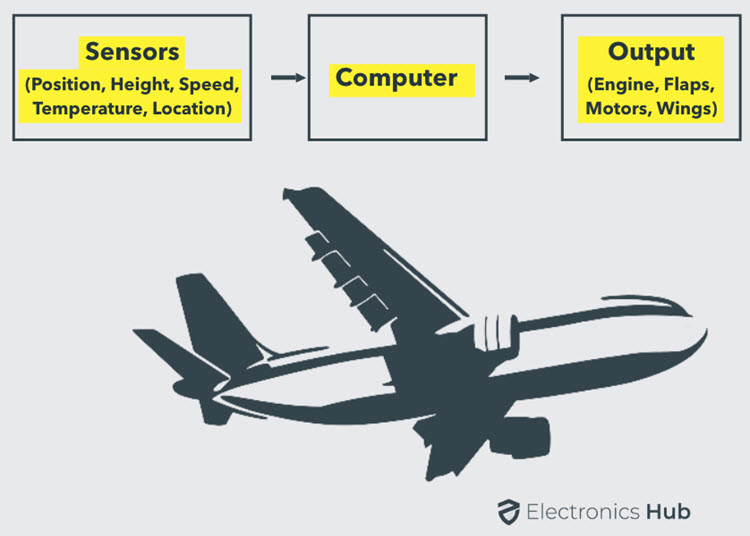
The example we are talking about here is the Autopilot System in aircrafts. Almost all civilian and military aircrafts have the feature of Automatic Flight Control system or sometimes called as Autopilot.
An Automatic Flight Control System consists of several sensors for various tasks like speed control, height monitoring, position tracking, status of doors, obstacle detection, fuel level, maneuvering and many more. A Computer takes data from all these sensors and processes them by comparing them with pre-designed values.
The computer then provides control signals to different parts like engines, flaps, rudders, motors etc. that help in a smooth flight. The combination of Sensors, Computers and Mechanics makes it possible to run the plane in Autopilot Mode.
All the parameters i.e., the Sensors (which give inputs to the Computers), the Computers (the brains of the system) and the mechanics (the outputs of the system like engines and motors) are equally important in building a successful automated system.
This is an extremely simplified version of Flight Control System. In fact, there are hundreds of individual control systems which preform unique tasks for a safe and smooth journey.
But in this tutorial, we will be concentrating on the Sensors part of a system and look at different concepts associated with Sensors (like types, characteristics, classification etc.).
In this article, we have seen about What is a Sensor, what are the classification of sensors and Different Types of Sensors along with their practical applications. In the future, I will update this article with more sensors and their applications.




52 Responses
Very interesting spacial for tilt sensor
One questions what function of tilt sensor in solar tiltsensor type tracker
Excellent. Brief but comprehensive.
Better pointers for details of design and access for ordering would be helpful.
Short simple informative.
thanks for this blog gives me such wonderful ideas how the circuits really works
It is a very impotent information for learning about sensor
Can we built a sensor for our requirements ?!!
yes we built a sensor as requirement.we should know about principle of physics that how does working
What is made the material of sensors
What is the good quality of sensor
English very best
Is there invisible sensors?
Could you help me to make a smart stick for blind people by voice message
it is build by arduino..and make programm by coding.
You mean the stick will be program by arduino?!! Also can Python be use for the coding?
I like this if posible u can sent in my email,thanks very much for understanding
Good article, but maybe you could have provided more examples in the post.
Thanks John.
I will try to update the post with more sensors and examples.
Can you please tell me. Which type of sensor using airport buggage conveyor belt
Very educative.
There is another movement sensor which wors on microwaves. It ischeap and penetrates woods, plastic but not metal. It detects only humans , animals body not all objects like ir. It can be found as radar sensor but is not radar even it works on microwaves.
I like this .this is useful for school and college students
Very interesting…
good informetion..thanks.
Was very helpful for my home work
Thank you so much Ravi sir thank you
can paper sensors be found?
It was very useful & informative.
Used information
super bro the she well all people
Very informative blog. My request is in the next blog please mention about good quality sensors in the market and how to get them. I am interested to provide them to some students in govt. schools so as to make the students experiment and learn the subject.
It is very exciting.
Really helped me to complete my homework…
Sitio con muy buenas propuestas para todos los amantes de electrónica, gracias por vuestros aportes.
Saludos mil
Please how does actuator manage the environment in motor car?
Trying to build a network of sensors for mechanical systems of a vehicle, using sensors. This is good but I need more clarification on sensors that work on rubber!
What kind of sensor can count the number of movement? Example squats.
thanks for your humble efforts .
Thank you for this article.T’was very useful
I’m researching to see if there is some type of object sensor available small enough to put on a dog collar that could help a blind pet. Any ideas would be appreciated.
Thank you for your effort,it is a basic information to engineering students.
Very brief, interesting and educative. We need more on practical aspects .I also need it in my email.
Yes It’s very excited to read
Thanks for you
Very handy, I’ve enjoyed every piece of this. Thank you in earnest.
Nice article about sensors. THanks a lot
Nice article about sensors. Thanks a lot
Thanks I gain from the article.
it has a good idea for electrical engineering
It’s a very good Article. As some one mentioned, it’s brief, but very informative. I’m tagging it for inclusion in my ‘POCKET’ Library. Saw Article in a PINTEREST E?MAIL.
Very educative article
Nice article, very infomative.
Thank you very much!
Was really helpful.
Thank you very much!
Was really helpful.
Easy to understand…Thank you very much
Thank you for sharing this knowledge with us. Very informative for technical student for learning.
What are our uses of thermal sensors in machines
Is their any sensor that detects only dry grain to pass through a machine that does not all wet products to pass through