A motherboard in a computer plays a vital role in the overall performance of the system. It is the backbone that connects all the essential components like CPU, GPU, RAM, hard drive, etc. together in one circuit board to successfully run the applications.
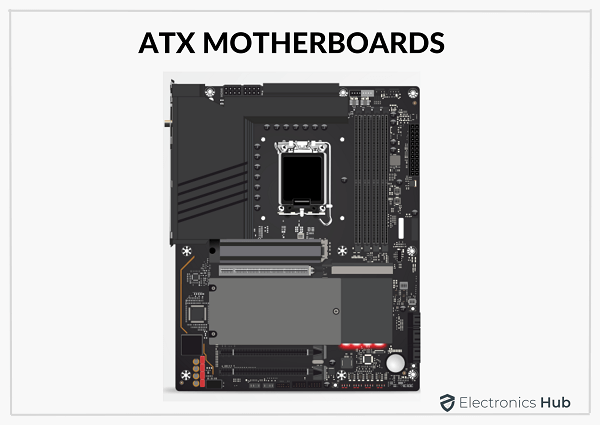
The layout and shape of a motherboard are called the form factor. It determines the case type, power supply, and where the essential components will fit. The most common type of form factor found in industrial and domestic PCs is ATX.
Advanced Technology eXtended or ATX is a motherboard that was introduced in 1995 by Intel to improve the standardization of motherboards.
ATX motherboards are available in different sizes and have slightly different functionality. They are Micro-ATX, Mini-ATX, WATX, EATX, mobile ATX, and pico-ATX. It is important to learn the difference between these variants because some features of one ATX form factor may not be suitable for another type.
In this article, we would like to discuss the differences between ATX and EATX i.e., Extended ATX form factor, and see which one you should buy. So, without further ado, let’s begin.
Outline
ToggleWhat is ATX?
Advanced Technology eXtended or ATX is the most common form factor of a computer motherboard. It was introduced by Intel in 1995 to replace the standard form factor motherboard i.e., AT or Advanced Technology.
ATX is considered one of the major changes in computer enclosure, power supply, and motherboard as it allowed interchangeability of parts and improved standardization. AT design, which is the predecessor of ATX, was once a de facto standard but lacked in many specifications.
This is where ATX proved better than AT in terms of interface, speed, expansion and overall performance. However, the arrangements of individual components on the ATX board blocked airflow and creates heat issues. To solve this problem, Intel introduced another form factor, BTX (Balanced Technology eXtended) in 2004.
In 2006, Intel discontinued the development of BTX due to the following reasons:
- People already invested in Advanced Technology eXtended (ATX) form factor and do not want any change in their system.
- BTX technology was expensive than ATX.
- Many users did not care too much about the cooling factor.
Due to these reasons, manufacturers and developers focused more on bringing ATX variations to the market. Most variants were smaller in size and the number of ports was reduced. However, the overall layout remained the same.
A full-sized ATX motherboard is 12 inches x 9.6 inches, which is the standard form factor of the mainboard. The dimensions of a Micro-ATX board are 9.6 inches x 9.6 inches making it a good option for a budget-friendly gaming PC.
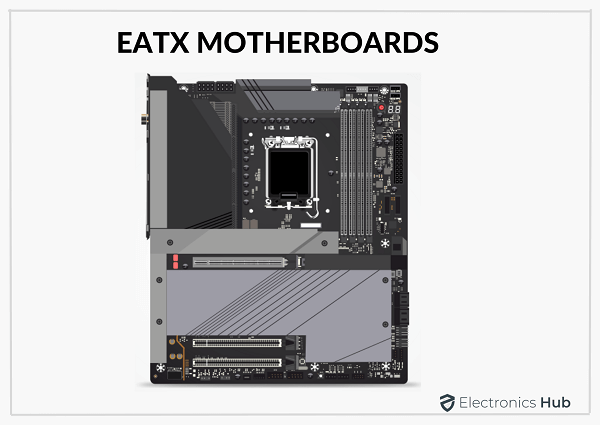
An EATX board, as the name suggests, is a bigger variant of the ATX form factor. It is 12 inches x 13 inches and offers all the ATX standard features. The advantages of having this motherboard are dual-socket support, better heat dissipation, additional slots, etc.
ATX Pros and Cons
Let us now see what advantages and drawbacks does an ATX form factor has:
Pros:
- ATX comes with many slots and ports that allow easy expansion.
- More number of ports and slots allow easy upgrade, without hindrance.
- ATX cases come in a variety of styles.
- Most gaming PCs are loaded with an ATX motherboard.
Cons:
- ATX board is heavy and large.
- The components arrangement in an ATX board disturbs airflow, thus less cooling.
- It is expensive.
What is EATX?
Extended ATX is the largest of all ATX variants. This motherboard is designed to build a powerful PC system. Its configuration allows it to work alongside full tower cases and provide ample space and features.
The massive size of this motherboard not only allows expansion but also offers a good breathing room for essential components. This affects the overclocking of the system, thus improving the performance.
EATX motherboards are perfect for enthusiastic gamers or professional production workers (graphic designers, video editors, etc.) However, to enjoy such utilities you will have to pay an enormous amount.
EATX Pros and Cons
If your budget is high and you care more about the performance, here are some advantages that you will get from an EATX. Plus, pay attention to the drawbacks to alter your decision.
Pros:
- It has a massive amount of space to install the memory.
- More expansion port means more GPUs, hence a better gaming experience.
- The large size of the board cools the components and offers fantastic overclocking.
Cons:
- It requires a heavy budget.
- EATX is not suitable for hobbyist gamers or editors unless you have a lot of money.
- Their large size and features can be a bit overkill for many users.
Difference between ATX and EATX
Let us see the differences between an ATX and EATX form factor with the help of a table representation.
| Features and Specs | ATX Motherboard | EATX Motherboard |
|---|---|---|
| Full-form | Advanced Technology eXtended | Extended ATX |
| Definition | ATX is the standard form factor of the motherboard. | EATX is nothing but a type of ATX with a bigger size. |
| Motherboard Type | As of 2021, it is the de facto standard of the motherboard. | EATX is the largest variant of the ATX board. |
| Cooling & Overclocking | ATX board arrangement can block the airway and affect cooling. | EATX, due to its massive size offers fantastic cooling and overclocking. |
| Price | ATX will cost less than EATX, but more than Micro-ATX. | Expensive than ATX |
| Current Status | It is common in domestic and industrial computers. | It is mostly used by competitive gamers or professionals. |
ATX VS EATX: Size
When we talk about ATX vs EATX, it is important to compare their sizes. An ATX motherboard which is the standard form factor has dimensions of 12 inches x 9.6 inches.
EATX, which is the largest variant of ATX is slightly bigger from the right side. It has dimensions of 12 inches x 13 inches. The larger size of this variant makes it a perfect option for server work.
As the size of the EATX board is larger, components installed in the board get good airflow, thus less heating. Plus, a system with an EATX mainboard is easier to use as the large size allows more space for GPU to fit in.
ATX VS EATX: Functionality
In terms of functionality, EATX performs better than ATX, how? Because EATX comes in a larger size, this means you get additional ports and slots for components.
In an ATX board, you will usually find 3-4 PCI-e x 16 ports and 4 RAM slots, whereas in an EATX board, you will find 4-8 PCI-e x 16 ports and 6-8 RAM slots.
Though EATX performs better than the ATX form factor, but is it suitable for all users? Well, let’s find out in the next section.
Which Should You Buy?
If you are confused about which motherboard should you go for, there is a rule of thumb to make your decision easy.
The type of motherboard you choose greatly depends on your needs. For example, if you are a hardcore competitive gamer, you will need a powerful PC system with dual graphics cards and better cooling, hence a larger motherboard (EATX). However, if you are a hobbyist gamer, a standard motherboard (ATX or smaller) should be fine for you.
The bottom line is, if you are willing to spend a large amount of money to upgrade from ATX to EATX, you can enjoy the following advantages:
- Better heat dissipation.
- Additional slots for more upgrades.
- Better gaming experience.
- Faster performance of various applications.
That being said, it will be wise to leave the EATX form factor for Professionals as this board can be overkill for many users.