Every electronic device we use in our daily life is one type of system. The systems working depending up on electronic variables like power or voltage or current is known as Electronic system. Number of blocks having different input – output relationship are connected together to form a system, which is supposed to execute a particular task or process.
Electronic System
An Electronic System is also referred as “Control system”. A system that is used to control or regulate the output of the other system is called control system. This is also a group or collection of different systems and blocks.
The industrial automations systems which are used in heavy industries are the example of control system. These are used to control the production process in industries.
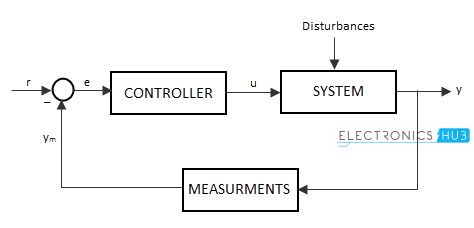
The block diagram of a basic control system, with control loop is shown below.
The input is connected to the controller to control the system output and the output of the controller is connected to the system or processor, which processes the output.
If the produced system output is deviated from the desired output, indicates that the system is encountered with some noise or error. The error signal is connected back to the controller, to make changes in the system according to system requirements.
A system can be represented in many ways such as pictorial manner, descriptive manner, schematic and mathematical manner etc. But many of the electronic systems are schematically represented by inter – connecting the individual blocks in series.
Each and every block of the system has its individual inputs and outputs. Each block in a control system will represent a system or an individual component of a system.
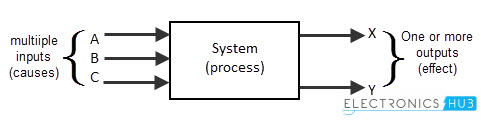
Block diagram of system of Electronic System
The block diagram for the simple system is shown below, with individual inputs and outputs
The electronic system may have multiple inputs and multiple outputs. The system accepts the inputs and it processes the required task to produce the outputs. The state of the system can be changed by processing the inputs. So the inputs are the “cause” of change in system’s equilibrium state.
This means the inputs and outputs of a system are in an direct relationship that inputs will show effect on outputs. This analysis of control system is called as “Cause and Effect analysis”.
An audio system, TV, or any Mp3 player is the example of an electronic system. The sound waves are converted to electrical signals and they are amplified to process the output of high strengthened audio signals, through speakers.
Example
We come across so many systems in our day to day life, such as washing machine, drier, keypad, Air conditioner etc. we use control systems mostly in industrial purposes like space technology, weapons, power systems and quality controlling of products like industrial automation etc.
Types of electronic systems
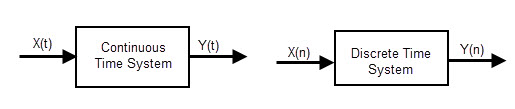
As we already explained earlier, every control system will have its own input and output. The input signal may be of continuous and discrete. Based on the input provided to the system, the control systems are classified into 2 types.
They are
- Continuous system
- Discrete system
Continuous system
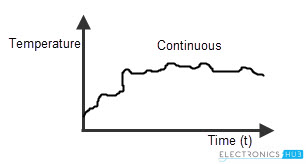
Continuous system is that in which the input signals are defined as the analog signals. The analog signals are continuous in nature, so they are called as “continuous time signals”.
The magnitude of the continuous signal will vary with the time period T. As the input is Analogues in nature, the continuous electronic systems produce the analogous output. This is the reason they are notified as “Pure analog systems”.
The values of the continuous electronic system varies only with time.
Example for continuous system
The process of measuring the temperature of a room is an example of continuous system. As the temperature is measured in a range of time duration, like Monday to Saturday or temperature levels from cold to hot etc, the temperature monitoring system is analog in nature or it is said to be an example of continuous electronic system.
Other examples of the continuous electronic systems are current and voltage signals, pressure, velocity and temperature signal etc.
Discrete system
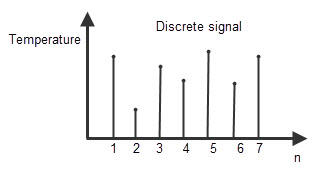
The discrete system is defined as the system having the sequence of discrete time values as its input. The values obtained at particular intervals of time are called “Discrete values”. As the input of discrete system is the sequence of instinctual values, the output will be in the form of sequence of numbers.
So these discrete systems are also known as “Digital systems”. Generally the output of digital system will be a binary number sequence, such as the collection of 0’s and 1’s.
One important thing about the discrete system is that, the discrete values defined at particular time intervals must be spaced equally. For example, if the time periods are t1, t2, t3, t4 and t5, then t1 – t2 = t2 – t3 = t3 – t4 = t4 – t5. The values of discrete system don’t vary over the time period, but changes at particular instances of time.
Example for Discrete system
The temperature measuring (monitoring) system which measures the temperature of room only at particular intervals of times, such as particular days like on Monday, on Tuesday or in particular time intervals like 1pm, at 2pm, at 3pm etc is the example of discrete time electronic system.
Representing continuous system as a set of discrete intervals
We can represent the continuous electronic system into discrete electronic system, by changing the domain of the system. This means, a continuous system with input and output signals as X (t) and Y (t) can be represented as discrete electronic system with input and output as X (n) and Y (t), where X (t) and Y (t) represents the time domain and X (n) and Y (n) represents the frequency domain
Interconnection of systems
The blocks of the electronic system can be connected with one another, to form more complex systems. This is called “Interconnection of blocks”. These interconnected blocks are about to perform the specific action or task. This interconnection is of two types
1) Parallel connection
2) Series connection
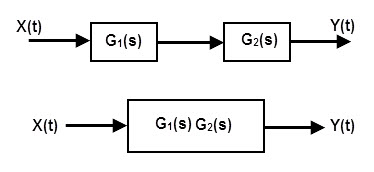
Series connected electronic system
The system formed by the series connection of the individual blocks is called as “Series connected system”. The output of the system formed by series connection of the two blocks is equal to the multiplication of the outputs of two individual blocks.
Let’s see the system below. Here a complex system is formed by connecting the two individual blocks, G1 and G2.
If the output of the system first system is G1 and the output of the system is G2 then the output of the series connected system is equal to Y (t) = G1(s)*G2(s).
If the system has 3 blocks A, B, C connected in series, then the output of the series connected system is equal to Y = A*B*C. We can apply this for any number of blocks in series.
Example: a micro phone connected with amplifier and speaker.
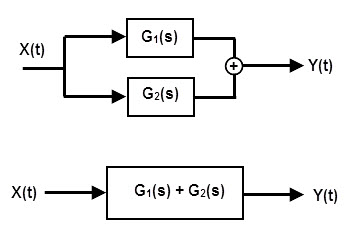
Parallel Connected Electronic System
The system formed by the parallel connection of the individual blocks is called as “Parallel connected system”. The output of the system formed by series connection of the two blocks is equal to the sum of the outputs of two individual blocks.
Let’s see the system below. Here a complex system is formed by connecting the two individual blocks, G1 and G2.
If the output of the system first system is G1 and the output of the system is G2 then the output of the parallel connected system is equal to Y (t) = G1(s) + G2(s).
If the system has 3 blocks A, B, C connected in series, then the output of the series connected system is equal to Y = A + B + C. We can apply this for any number of blocks in parallel.
Example: several micro-phones connected with single amplifier and to a single speaker system.
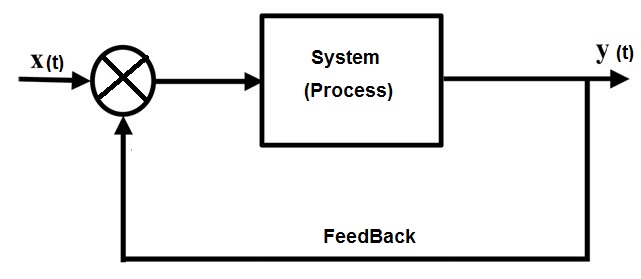
Electronic feedback systems
Feedback is another type of interconnection of systems. Feedback loop means connecting some part of output value connecting back to the input. The electronic systems having a connected feedback loop are called “Closed feedback system”.
.
The feedback loop allows the system to check errors and avail it to auto correct the errors occurred in its output. So these systems are more stable than open loop systems (which doesn’t contain any feedback loop).
Based on the nature of the feedback loop, the closed loop systems classified as positive feedback systems and negative feedback systems.
The system in which the feedback loop increases the level of output of the system is known as “Positive feedback electronic systems”. Similarly, the system in which the feedback loop decreases the level of output of the system is known as “Negative feedback electronic systems”.
Example: An automatic heating system is an example of the simple feedback system.


One Response
Thanks electronics hub. Have learned a lot from you