PCIe x16 is a term you might have come across while upgrading your computer, but what does it really mean? For many, understanding technical jargon like PCIe x16 can be confusing and frustrating, especially when trying to figure out if it’s essential for their system.
In this blog post, we’ll break down what PCIe x16 is, why it’s important, and how it impacts your computer’s performance. Whether you’re a casual user or a tech enthusiast, this guide will help you make sense of PCIe x16, so you can make informed decisions without feeling overwhelmed by the details.
Outline
ToggleWhat Is PCI Express?
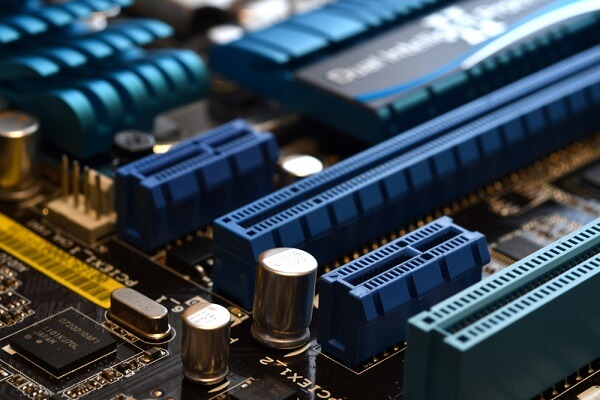 PCI Express, or PCIe is a way to connect fast parts inside your computer. It’s used for things like graphics cards, SSDs, and Wi-Fi cards. These connect to the motherboard, which is the main board in your computer.
PCI Express, or PCIe is a way to connect fast parts inside your computer. It’s used for things like graphics cards, SSDs, and Wi-Fi cards. These connect to the motherboard, which is the main board in your computer.
PCIe lets these parts talk directly to the CPU, which makes everything faster and smoother. This speed is important, especially for games or programs that need a lot of data.
Motherboards have PCIe slots in different sizes. These sizes are called x1, x4, x8, or x16. The bigger the number, the faster the data moves, and the bigger the card it can fit.
Over time, PCIe has gotten better and faster with new versions. This makes it a good choice for both old and new technology.
What Do You Mean By The PCIe x16?
The PCIe x16 slot is a connection on computer motherboards, made for high-speed parts that need a lot of bandwidth. The “x16” means the slot has 16 lanes for data transmission, with each lane having wires for sending and receiving data.
Here’s why the PCIe x16 is important:
- Maximum Bandwidth: This slot allows a large amount of data to move between the component and the computer. It’s great for graphics cards, which need to handle lots of visual data.
- Performance: Devices connected to a PCIe x16 slot can work at their best because of the high bandwidth. This is ideal for gaming, graphics work, and heavy data tasks.
- Compatibility And Versatility: PCIe x16 slots can also work with cards that have fewer lanes (like x8 or x4), though they will have less bandwidth. This flexibility makes it easier to build or upgrade computers for different needs.
In short, the PCIe x16 slot is key for high-performance tasks, offering the fastest transfer speeds in a PCIe setup, making it essential for gaming and professional workstations.
Applications Of PCIe x16 Slots
PCIe x16 slots are versatile due to their high bandwidth and fast data transfer capabilities. Here are some of their main uses:
- Graphics Cards: The most common use for PCIe x16 slots is connecting graphics cards (GPUs) to the motherboard. GPUs need high data bandwidth to handle tasks like 3D graphics, video editing, and animation. PCIe x16 slots provide the necessary speed for smooth visuals, making them crucial for gamers, content creators, and visual design professionals.
- High-Performance Networking Cards: PCIe x16 slots are also used for connecting powerful networking cards, especially in data centers, servers, and workstations. These cards offer features like multiple Ethernet ports and low-latency communication, making them ideal for tasks that involve heavy data loads, such as large-scale data transfers and cloud computing.
- High-Speed Storage Devices: PCIe x16 slots can accommodate fast storage devices, like NVMe SSDs, which offer much faster data transfer rates than traditional SSDs. This makes them perfect for tasks where storage speed is crucial, such as video editing and database management.
- Specialized Accelerator Cards: PCIe x16 slots are used for specialized cards that enhance system performance by offloading tasks from the CPU. Examples include FPGA cards for hardware acceleration, AI accelerators for machine learning, and HPC cards for scientific simulations. These cards use the high bandwidth of PCIe x16 slots to boost performance in specific applications.
Versions Of PCIe x16 Slot
The PCIe x16 slot is a crucial component in computer hardware, especially for those who require high bandwidth for applications like gaming, video editing, and machine learning. Here’s a breakdown of the different versions of the PCIe x16 slot, which highlight their evolution and capabilities:
1. PCIe Version 1.0
- Release Year: 2003
- Data Rate:5 GT/s
- Bandwidth Per Lane: 250 MB/s
- Total Bandwidth: 4 GB/s
- Key Features: Introduced the concept of serial communication in contrast to the parallel method used in previous standards.
2. PCIe Version 2.0
- Release Year: 2007
- Data Rate: 5 GT/s
- Bandwidth Per Lane: 500 MB/s
- Total Bandwidth: 8 GB/s
- Key Features: Doubled the bandwidth of PCIe 1.0, improved protocol efficiency with better encoding.
3. PCIe Version 3.0
- Release Year: 2010
- Data Rate: 8 GT/s
- Bandwidth Per Lane: 985 MB/s
- Total Bandwidth:75 GB/s
- Key Features: Introduced a more efficient encoding scheme (128b/130b), significantly increasing the data rate without changing the clock frequency.
4. PCIe Version 4.0
- Release Year: 2017
- Data Rate: 16 GT/s
- Bandwidth Per Lane:969 GB/s
- Total Bandwidth:5 GB/s
- Key Features: Doubled the data rate of PCIe 3.0, supporting advanced GPUs and NVMe SSDs with greater efficiency.
5. PCIe Version 5.0
- Release Year: 2019
- Data Rate: 32 GT/s
- Bandwidth Per Lane:938 GB/s
- Total Bandwidth: 63 GB/s
- Key Features: Continued to double the bandwidth, aimed to meet the demands of AI and machine learning hardware.
6. PCIe Version 6.0
- Release Year: Expected around 2021-2022
- Data Rate: 64 GT/s
- Bandwidth Per Lane:876 GB/s
- Total Bandwidth: 126 GB/s
- Key Features: Plans to utilize PAM-4 encoding, which allows for higher data rates by transmitting multiple bits per symbol.
Each iteration of the PCIe x16 slot significantly increases the potential for faster data transfer, accommodating the growing demands of modern computing tasks and paving the way for future innovations in hardware technology.
|
PCIe Generation |
x1 |
x2 |
x4 |
x8 |
x16 |
|
1 |
0.25 GBps |
0.5 GBps |
1 GBps |
2 GBps |
4 GBps |
|
2 |
0.5 GBps |
1 GBps |
2 GBps |
4 GBps |
8 GBps |
|
3 |
0.9 GBps |
1.9 GBps |
3.9 GBps |
7.8 GBps |
15.7 GBps |
|
4 |
1.9 GBps |
3.9 GBps |
7.8 GBps |
15.7 GBps |
31.5 GBps |
|
5 |
3.9 GBps |
7.8 GBps |
15.7 GBps |
31.5 GBps |
63 GBps |
What Are The Different Types Of PCIe Slots?
PCI Express (PCIe) slots are key parts of a motherboard that connect high-speed devices to the computer. Each slot has one or more lanes, with each lane made up of pairs for sending and receiving data, called PCI lanes. The common PCIe slots are x1, x4, x8, and x16, showing how many lanes they support.
- PCIe x1 Slot: This slot has one lane and is used for devices with lower data needs, like sound cards or network cards.
- PCIe x4 Slot: This slot has four lanes and offers more bandwidth, suitable for devices like SSDs or RAID cards.
- PCIe x8 Slot: This slot, with eight lanes, is used for devices needing more data but not the full capacity of x16, such as network cards or mid-range storage controllers.
- PCIe x16 Slot: This is the widest and fastest slot, with sixteen lanes, used for high-end graphics cards or other high-performance devices.
Each PCIe slot type is designed to meet different performance needs, allowing devices to operate effectively. This modular system offers flexibility and allows for easy upgrades in the future.
FAQs:
Whether you need a PCIe x16 slot depends on your specific requirements. For example, If you are building a gaming PC or working with graphics-intensive applications such as video editing, 3D modeling, or CAD software, a PCIe x16 slot is essential. Also, if you are planning to use multiple graphics cards in a multi-GPU setup, a PCIe x16 slot is required for each GPU.
The main difference between PCIe and PCIe x16 lies in their physical configurations and the number of data lanes they support. PCIe is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard that allows various hardware components to communicate with the motherboard. On the other hand, PCIe x16 means a specific configuration of the PCIe slot with 16 data lanes.
The “x16” in PCIe x16 stands for the number of data lanes available in the slot. It represents the physical configuration of the slot and indicates how many separate data pathways are available for communication between the motherboard and the connected device.
In the case of PCIe x16, there are 16 data lanes in the slot. Each data lane is capable of bidirectional data transfer, meaning data can flow in both directions simultaneously. These lanes act as individual pathways through which data travels to and from the connected device, such as a graphics card.
Whether a PCIe x16 slot can operate at its full speed depends on several factors such as the version of the PCIe standard supported by the slot, the specific hardware components connected to the slot, and any potential limitations imposed by the motherboard. If both the motherboard and the device support the same PCIe version (e.g., PCIe 5.0), the slot can operate at the full speed designated by that version.
In certain cases, the motherboard’s BIOS may have settings that affect the PCIe slot speed. For example, some motherboards allow users to manually set the PCIe mode to a specific version.
Conclusion
PCIe is a standard connectivity port on the motherboard that connects hardware components to the motherboard, with the PCIe x16 slot being particularly important for graphics cards and high-bandwidth devices. The PCIe version determines data transfer speed, with newer versions offering increased performance. In this guide, you can also find comparisons of different PCIe versions from 1.0 to 6.0 along with their respective data transfer rates. However, whether you need a PCIe x16 slot depends on usage, such as gaming and graphics-intensive tasks. If the motherboard and connected device support the same PCIe version and use all 16 lanes, the PCIe x16 slot will be able to operate at its full speed, offering numerous benefits with all connected devices.

