Soldering plays a vital role in modern electronics and numerous other industries. It involves joining metal components by melting solder, a metal alloy, to create a strong electrical and mechanical bond. A soldering iron tip serves as a crucial component in the soldering process. This small, pointed piece of metal attaches to the soldering iron and directly contacts the solder and workpieces. The tip’s quality and condition significantly impact the efficiency and precision of soldering tasks.
Have you just bought a soldering iron for some DIY Projects but are confused about choosing between a chisel or a conical tip? Or perhaps you need to do some very detailed work but you know you can’t with the knife iron tip that you already own? In this article, we aim to dispel such questions and some other common queries regarding soldering iron tips.
Outline
ToggleA Brief Note on Soldering
Soldering, a fundamental skill in electronics and metalwork, involves joining metal components using molten metal alloy, known as solder. The process requires a soldering iron, a tool with a heated tip that melts the solder and creates the bond. It serves as the backbone for assembling electronic circuits. Several factors influence a successful soldering project including the choice of solder, flux, and most importantly, the soldering iron tip.
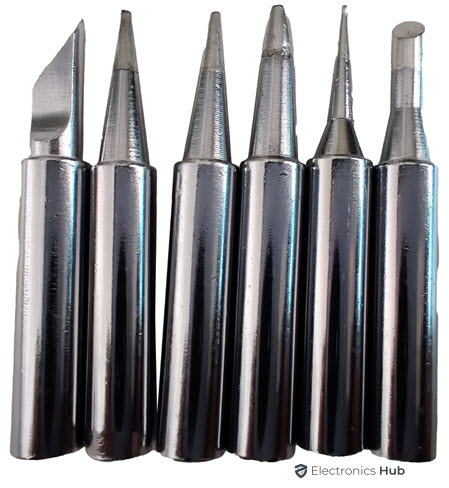
Speaking of soldering iron tips, they come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each designed for specific tasks. For instance, conical tips are ideal for precision work, while chisel tips are better suited for broader connections. Moreover, the material of the tip, commonly copper core with iron plating, affects its heat conductivity and durability. It is removable and reusable. There are many tips available in the market. We first look at the different types of soldering iron tips available. Later, we will understand their uses, sizes, prices, and cleaning procedures.
Types of Soldering Iron Tips
Different types of soldering iron tips have varied sets of applications from assembling electronic components on printed circuit boards (PCBs) to making jewelry. In this section, we will look at the most common soldering iron tips.
1. Conical or B-series Tips
The conical series tips are so named because of their pointed cone-like shape. Since it has a very rounded tip, soldering can be done from any angle, and hence this tip is used for general purposes.
2. Chisel or D-series Tips
The name of the D-series type arises from its shape which is that of a chisel. Just like the conical iron tips, these are used for general purpose soldering. The surface area is larger as compared to conical tips – more heat is transferable from the tip to the electrical component and for a quick DIY, this is the tip you would want to pick. They are especially helpful in soldering thick wires.
These tips come in various sizes, so make sure to choose one which is an appropriate size. If you choose one that’s too large, then you may end up having the solder flow from one point to another creating a sort of a bridge. One that’s too small would not help you reach all the points you want to.
3. Knife or K-series Tips
The knife soldering iron tip comes with a slanted tip resembling the shape of a knife. It is great for drag soldering and fixing solder bridges. It is not impossible to do point soldering with this tip, but it is considerably difficult as compared to the other tips.
4. Bevel or C-series Tips
The Bevel or C-series tips are used for drag soldering as it can hold more solder. It has a curved surface, resembling that of a ground-up chalk-piece or pencil. You can spread out solder on the tip and even apply small amounts on various points whether they are far apart or in close proximity.
5. Needle or I-series Tips
The I series or needle type soldering iron tip is very pointed and was manufactured to do very detailed work. It is not suitable for soldering large components as it transfers relatively very less heat as compared to other tips.
6. Specialized Tips
Some manufacturers make specialized soldering iron tips, e.g., the spade tip is used to scrape UV glue off from glass surfaces such as an LCD screen.
Tunnel Shape and Spatula Shape Tips are also available from some manufacturers. These Soldering Iron Tips are very useful for SMD work.
7. Advanced Soldering Iron Tips
a. Tips with Integrated Heating Elements
Unlike traditional soldering iron tips, which rely on external heating elements to transfer heat, these advanced tips feature built-in heaters. This design enhances heat transfer efficiency, allowing for faster heat-up times and more precise temperature control.
Integrated heating element tips eliminate the need for bulky heating elements within the soldering iron, resulting in a more lightweight and ergonomic design. Furthermore, they offer improved thermal stability, maintaining consistent temperatures across the entire tip surface for uniform soldering performance.
b. Smart Tips with Temperature Sensing
Smart soldering iron tips equipped with temperature sensing capabilities incorporate sensors that monitor and adjust the tip’s temperature in real-time for precise temperature control throughout the soldering process.
Temperature sensing tips eliminate the guesswork associated with manual temperature adjustment.
c. Tips for Lead-Free Soldering
With increasing environmental regulations and concerns about lead exposure, there has been a growing demand for soldering iron tips specifically designed for lead-free soldering. These tips are engineered to withstand the higher temperatures required for lead-free solder alloys while maintaining durability and performance.
Lead-free soldering tips may feature specialized coatings or materials that offer enhanced resistance to corrosion and oxidation, ensuring longevity in demanding soldering environments.
Choosing The Right Soldering Tip
Here are some pointers in choosing a soldering iron tip.
- Choose a tip that is compatible with your soldering iron.
- Determine the type based on whether you wish to do detailed work, general-purpose soldering, or drag soldering.
- Determine the size – if it’s too small, there will not be enough heat transfer and if it is too large, you could damage the board.
- Temperature requirements play a significant role in tip selection. Certain soldering jobs may require higher or lower temperatures, necessitating the use of tips designed to withstand specific temperature ranges
If you are just learning how to solder, then avoid choosing a conical tip. Beginners tend to apply more pressure aiming to increase the flow of solder – a classic mistake that can end up damaging the board.
Choose a chisel tip that is ideal for through-hole, wire, de-soldering, and surface mounts.
The following table lists out some popular Solder Iron Tips along with their common applications.
| Soldering Iron Tip | Application |
| Conical – B Series Tip | Working in tight spaces between components, for narrow pitch with tall ICs around |
| Chisel – D Series Tip | General-purpose, heavy-duty soldering, |
| Bevel – C Series Tip | Drag Soldering, general purpose |
| Knife – K Series Tip | Drag Soldering, Fix Solder Bridges |
| Needle – I Series Tip | For narrow pitch soldering |
| J Series Tip | For angled narrow pitch soldering |
| Tunnel Shape Tip | For working on SMD Components |
| Spatula Shape Tip | For SMD works |
Things to Keep In Mind While Soldering
- Avoid using too much pressure as it may damage the tip or the board.
- Never use brute force on the tip (using it as a screwdriver or to pull up components).
- If you are a beginner, then use the lowest possible temperature to avoid premature wear and tear.
- Turn off your soldering station or iron when you are not using it.
Taking Care of Soldering Iron Tips
Poor maintenance of soldering iron tips is the main reason for soldering problems. To make sure that your soldering iron lasts longer, you may consider the following instructions.
Use High Quality Solder
One of the best ways to ensure that your tip lasts longer is to use high quality solder. Low quality solder contains impurities that can build up with use over time and prevent efficient heat transfer. Choose from good brands and test the solder by melting it at a chosen temperature. Good quality solder melts readily and completely at the recommended temperature. Do read the manufacturer’s instructions to check how the solder is expected to perform.
Maintain Optimal Temperature
Soldering stations have temperature regulators that can help you maintain the optimal temperature to extend the life of the tip and iron. These regulators adjust the temperature and whenever it falls below or exceeds the range. Some soldering irons have more accurate temperature regulators than others.
Clean Soldering Iron Tips
Before soldering, clean your tip with a clean cloth and some alcohol. This helps remove impurities such as remnants of solder from previous projects, grease, oxidation, etc. If there’s a stubborn piece of contaminant left on the tip, you can use metal wool to gently scrape it off. Cleaning wool does not reduce the temperature of the tip. After cleaning, apply some fresh solder to prevent oxidation. For heavy-duty soldering, you can use a polishing bar.
Use Flux To Prevent Oxidation
To avoid the formation of an oxidation layer, you can use soldering flux. Flux is a substance that dissolves the oxidation layer and it comes in a paste form (more common but liquid-form is also available). It allows you to work without any hindrance. We recommend using a flux when doing any kind of soldering work followed by some intensive cleaning. Alternatively, you can use no-clean flux, which as the name suggests, does not require much cleaning.
Tinning Your Tips
Always tin your tips before and after soldering. To ‘tin’ your tip, just cover it with a thin layer of solder. This is a protective layer that prevents oxidation. It helps the solder wire melt and flows better, increasing the efficiency of the heat transfer.
Storing Soldering Iron Tips
Proper storage is crucial for protecting soldering iron tips from damage and oxidation. After each use, clean the tip and apply a fresh coat of solder to prevent oxidation during storage.
Store the soldering iron in a designated holder, stand, or a sealed container to protect the tip from physical damage and prevent accidental burns. Additionally, consider using tip covers or sleeves to further shield the tip from environmental contaminants and prolong its lifespan.
Soldering Iron Tip Accessories
You can enhance the soldering experience and prolong the lifespan of soldering iron tips by investing in some simple accessories.
1. Tip Cleaner Stations
These stations typically consist of a base with a sponge and a receptacle for holding brass wire cleaner. During soldering, users can quickly clean the tip by wiping it on the damp sponge to remove excess solder and flux residues.
The brass wire cleaner provides additional scrubbing action to remove stubborn debris and oxidation buildup from the tip’s surface.
2. Tip Holders and Stands
These accessories typically feature a heat-resistant base with a slot or cradle to securely hold the soldering iron. By placing the iron in the holder or stand between soldering tasks, users can prevent accidental burns and damage to work surfaces.
Tip holders often include compartments for storing spare tips for easy access and organization.
3. Soldering Stations with Advanced Tip Management
Some advanced soldering stations include automatic sleep modes or standby functions to conserve energy and prolong tip life when the iron is not in use. As soon as you insert the soldering iron between task into the stand, a sensor will detect this and put the iron to sleep mode.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the essential aspects of soldering iron tips and their significance in the soldering process. We discussed the different types of tips, factors to consider when choosing the right tip for various applications, and the importance of maintaining soldering iron tips through proper cleaning, tinning, and storage practices.
Hope this information has helped you and stay tuned for more!











One Response
Can I use a brass soldering tip for soldering wires and electronics?